- November 7, 2024
- Posted by: admin
- Categories: Channel Financing, Blog

Factoring is a financial service that helps businesses unlock working capital by selling their trade receivables to a financial institution, commonly referred to as the “factor.” In simple terms, it is a solution for businesses looking to address immediate cash flow needs without waiting for customer payments. The seller of goods or services, known as the client, enters into a relationship with the factor, who then provides an advance of 80% to 90% of the receivables’ value. This helps businesses maintain liquidity and operate smoothly without the worry of delayed payments.
Factoring is particularly beneficial in international trade, where the factor may involve a counterpart from the importer’s country to manage risks. For businesses, especially those involved in exports, this financial tool offers quick access to cash, allowing them to meet operational needs. After adjusting costs like service charges, the remaining balance is paid to the seller when the invoice matures.
In essence, factoring is a practical way for businesses to convert credit sales into immediate cash flow.
Why Factoring is Growing in Popularity?
Factoring has steadily gained traction as an alternative to more traditional forms of trade finance, such as letters of credit (LCs) or bank loans. Its popularity stems from the unique benefits it offers, particularly to small businesses and exporters looking to maintain consistent cash flow.
Let’s explore the advantages of factoring that make it such an appealing choice for businesses.
Advantages of Factoring
1. Immediate Cash Flow
One of the biggest advantages of factoring is the quick access to cash. Factoring companies typically advance up to 80% to 90% of the invoice amount within one to two working days. This significantly reduces the time businesses spend waiting for payments, allowing them to manage their working capital efficiently.
2. No Need for Collateral
Unlike traditional bank loans that often require businesses to provide collateral, factoring does not require additional assets. Since the factor assumes the risk by purchasing the receivables, small businesses don’t have to worry about securing collateral, making it a more accessible financing option.
3. Focus on Core Business Activities
Factoring saves businesses time and effort by managing the collection of payments. This allows companies, particularly smaller ones, to focus more on their core business activities. The factor handles everything related to sales ledger management, credit control, and collection of payments, enabling business owners to devote more time to growth and innovation.
4. A Sale, Not a Loan
Factoring is different from a loan because it doesn’t create debt on the balance sheet. It involves selling receivables, meaning the business doesn’t take on additional liabilities. This contrasts with options like bill discounting, where bills are simply used as collateral for loans.
5. Advisory Services
Factoring companies often provide valuable insights and advice, especially for businesses engaged in international trade. Factors typically have knowledge of different buyers and regions, helping exporters assess credit risks and negotiate favorable terms. By evaluating the creditworthiness of buyers, factoring companies can help businesses avoid high-risk transactions, providing peace of mind when dealing with unfamiliar markets.
6. Protection from Bad Debts
Non-recourse factoring offers protection against bad debts. In this arrangement, the factor takes on the risk of non-payment, allowing businesses to focus on their growth rather than worrying about whether they’ll be paid. While non-recourse factoring can be slightly more expensive, the benefit of reduced risk makes it an attractive option for many businesses.
7. Cost-Effective
In the competitive factoring industry, costs are generally reasonable. Recourse-based factoring tends to be particularly cost-effective, and even non-recourse factoring, though more expensive, offers significant value by reducing risk. With factoring, businesses can efficiently manage their sales ledger functions without the high costs associated with other financing methods.
8. Fast and Simple Process
Factoring is widely appreciated for its simplicity and speed. Businesses often need working capital quickly to keep operations running smoothly. Traditional bank loans can take time to secure, with long application processes. In contrast, factoring requires a much simpler application and approval process, making it a quicker option for growing companies.
9. Higher Credit Limits
Most factoring companies set a credit limit for their clients, but these limits are usually generous enough to meet the needs of small to medium-sized businesses. For example, Drip Capital, a leader in export factoring, offers a credit limit of up to $2.5 million, allowing businesses to access significant working capital.
Disadvantages of Factoring
While factoring offers numerous benefits, it’s important to consider some potential drawbacks.
1. Non-Recourse Factoring Can Be Costly
Non-recourse factoring, where the factor assumes the risk of bad debts, tends to be more expensive than recourse factoring. Interest rates for non-recourse factoring can start at around 0.7% per month, and pricing depends on the risk profile of the business and its customers. Despite this higher cost, for many businesses, the quick access to cash and the risk protection it offers can make non-recourse factoring worth the expense.
Also Read: Recourse vs Non-Recourse Factoring
2. Receivables Can’t Be Used as Collateral Elsewhere
When businesses sell their receivables to a factor, they no longer control those receivables. This means they can’t use them as collateral for other financing services, limiting their options for securing additional funds.
3. Service Continuity Depends on Creditworthiness
Factoring relies heavily on the creditworthiness of the buyer. Factors perform ongoing risk assessments and may reject invoices if they believe a buyer is no longer creditworthy. This can disrupt the factoring arrangement and cause issues for the business, especially if the business and the factor have differing opinions on the buyer’s reliability.
4. Lack of Personal Touch
Some buyers may feel uncomfortable with a third party—such as a factoring company—managing their payments. In certain cases, importers may prefer dealing directly with the seller, which could impact the business relationship.
Bank Loans vs. Factoring
To fully understand the advantages of factoring, it’s essential to compare it with traditional bank loans.
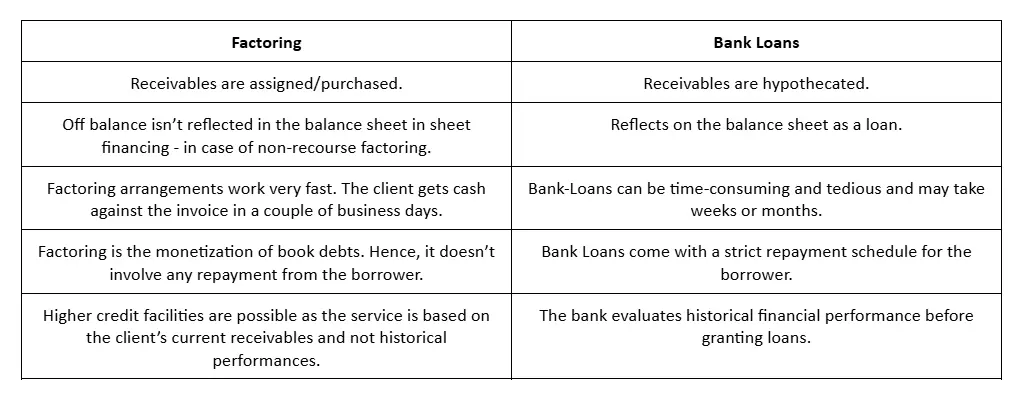
- Collateral: Unlike bank loans, factoring does not require collateral, making it more accessible to small businesses.
- Speed: Factoring provides faster access to working capital compared to the lengthy process of obtaining a bank loan.
- Debt-Free Financing: Factoring doesn’t create debt on a business’s balance sheet, while bank loans do.
- Flexibility: Factoring is more flexible, particularly for businesses with fluctuating cash flow needs, whereas bank loans may offer fixed financing.
Conclusion: Is Factoring Right for You?
Factoring is an ideal solution for businesses that need quick access to working capital, especially those involved in export and trade. It offers immediate cash flow, eliminates the need for collateral, and provides valuable advisory services. With factors like Credlix, businesses can unlock the full potential of factoring, with experts guiding them through every step of the process.
If you’re looking for a cost-effective way to manage your cash flow and protect yourself from bad debts, factoring could be the perfect fit for your business needs.
Also Read: Export Factoring Advantages and Disadvantages