[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text][/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row el_class=”padding-sm-bottom-40″][vc_column offset=”vc_col-lg-8 vc_col-md-8″ el_class=”post-details-sec”][vc_single_image image=”12098″ img_size=”full” css=”.vc_custom_1707891234357{margin-bottom: 44px !important;}”][vc_row_inner css=”.vc_custom_1608297138483{margin-bottom: 0px !important;}”][vc_column_inner][vc_column_text]Welcome to the dynamic realm of Recourse Factoring, a financial strategy that revolutionizes traditional approaches to business financing. Recourse Factoring, at its core, is a distinctive method enabling businesses to unlock the potential of their accounts receivable. Unlike conventional factoring, this innovative concept empowers companies to regain control over their outstanding invoices by offering recourse options.
In essence, Recourse Factoring provides a unique blend of flexibility and financial security. Through this strategic approach, businesses can access immediate cash flow while retaining the ability to address any potential payment disputes.
This introduction marks the beginning of a journey into the intricate world of Recourse Factoring, where companies navigate the balance between liquidity and risk management. Join us as we delve deeper into the nuances of this financial tool, discovering how it reshapes the landscape of modern business financing.
What is Recourse Factoring?
Recourse Factoring is a financial strategy that allows businesses to optimize cash flow by leveraging their accounts receivable. In this method, a company sells its unpaid invoices to a factor, unlocking immediate funds. What sets Recourse Factoring apart is the option for the business to repurchase the invoices if the customer fails to fulfill payment, providing a safety net against defaults.
This dynamic approach offers a balance between quick access to working capital and the ability to mitigate potential risks associated with outstanding payments, making it a flexible and strategic financing solution for businesses.
An Example of Recourse Factoring
Consider a manufacturing company facing a cash flow crunch due to delayed customer payments. Opting for Recourse Factoring, the business sells $100,000 worth of unpaid invoices to a factor at a discount, receiving an immediate infusion of capital. The factor assumes the responsibility of collecting payments from the customers.
However, if a customer fails to pay within the agreed-upon timeframe, the recourse provision kicks in. The manufacturing company has the option to repurchase the delinquent invoice from the factor, absorbing the associated risk. This flexibility allows the business to address short-term financial needs while retaining control and recourse in case of any payment discrepancies, showcasing the strategic advantage of Recourse Factoring.
Features of Recourse Factoring

Recourse Factoring exhibits distinctive features that set it apart as a strategic financial tool for businesses.
Higher Advance Rates
In Recourse Factoring, businesses enjoy elevated upfront funding, as the risk is borne by the company rather than the factoring entity. This means that a larger percentage of the invoice value is advanced, providing immediate access to a significant portion of the accounts receivable.
Cheaper Factoring Fee
One notable advantage of Recourse Factoring lies in its cost-effectiveness. The factoring fee associated with this method tends to be lower compared to non-recourse factoring. This financial efficiency enhances the overall attractiveness of recourse factoring as a viable financing solution.
Quick Funding
The inherent risk association with the business in recourse factoring expedites the funding process. With the burden of risk on the company, documentation and approval procedures are streamlined, ensuring swift access to the much-needed working capital.
Easy Eligibility Criteria
Recourse Factoring comes with accessible eligibility criteria. Factoring companies focus more on the credit history of the customers rather than stringent requirements for the seller. This flexibility in eligibility enhances the feasibility of recourse factoring for a diverse range of businesses, fostering inclusivity in its application.
How Does Recourse Factoring Work?
Here’s how recourse factoring works:
Invoice Submission
The company submits its invoices to a factoring entity, initiating the recourse factoring process. The company decides between recourse and non-recourse based on the buyer’s credit history.
Risk Assessment
The buyer’s credit history plays a crucial role in this decision-making process. If the buyer has a positive credit history, indicating timely payments, the company may opt for recourse factoring, assuming the risk themselves.
Percentage Advance
Upon submission of the invoice, the factoring company promptly provides the business with a percentage of the invoice amount. This immediate advance assists the business in managing its working capital needs.
Payment Collection
As the invoice due date approaches, the factoring company takes responsibility for collecting the payment directly from the buyer. If the buyer pays on time, the process concludes smoothly.
Liability in Recourse Factoring
In recourse factoring, if the buyer fails to pay, the business becomes liable. The business must repay the invoice amount to the factoring company, which can then attempt to recover the amount from the buyer.
Undisclosed Factoring
Recourse factoring may involve undisclosed arrangements, where the buyer remains unaware of the agreement between the business and the factor.
Non-Recourse Option
For buyers with a poor credit history or a track record of delayed payments, businesses may choose non-recourse factoring. In this scenario, the factoring company assumes the risk, and the business receives payment at a discounted rate.
Working Capital Utilization
In both recourse and non-recourse factoring, the business leverages the received funds, often at a discounted rate, to sustain and enhance its working capital.
Benefits of Recourse Factoring
Recourse factoring is a type of factoring arrangement where the factor has the right to recourse against the seller (client) in case the debtor (customer) fails to pay the invoice. Here are ten potential benefits of recourse factoring:
Higher Advance Rates: Recourse factoring often allows for higher advance rates compared to non-recourse factoring. This means the client can receive a larger percentage of the invoice amount upfront, providing improved cash flow.
Lower Fees: Recourse factoring usually comes with lower fees and costs compared to non-recourse factoring, making it a more cost-effective financing solution for the client.
Easier Approval: Recourse factoring may be more accessible for businesses with a higher risk profile, as the factor is protected by the recourse clause in case of non-payment by the debtor.
Flexible Terms: Recourse factoring arrangements can be more flexible in terms of contract terms and conditions, allowing businesses to tailor the agreement to their specific needs and circumstances.
Credit Risk Mitigation: While the client retains credit risk in recourse factoring, the factor can still provide valuable credit information and monitoring services to help the client assess the creditworthiness of their customers.
Customized Collections: With recourse factoring, the client often maintains control over the collection process. They can choose to handle collections in-house or work closely with the factor to ensure a customer-friendly approach.
Preservation of Customer Relationships: Since the client maintains control over collections, they have the opportunity to preserve their relationships with customers, which may be crucial for repeat business and long-term success.
Cost-Effective Financing: Recourse factoring can be a more affordable financing option for businesses compared to traditional bank loans or other forms of financing, especially for those with a higher risk profile.
Quick Funding: Recourse factoring transactions can be processed quickly, providing the client with rapid access to funds. This agility is beneficial for businesses with immediate cash flow needs.
Tailored Solutions: Recourse factoring arrangements can be tailored to fit the unique needs of the client’s business. This customization allows for a more personalized and effective financing solution.
Disadvantages of Recourse Factoring
While recourse factoring offers certain benefits, it also comes with its share of disadvantages. Here are some potential drawbacks of recourse factoring:
Credit Risk Retention: In recourse factoring, the client retains the credit risk for non-payment by the debtor. If the customer fails to pay the invoice, the client is responsible for repurchasing the debt, which could result in financial losses.
Financial Exposure: The client faces the risk of financial exposure if the debtor becomes insolvent or experiences financial difficulties. This exposure can impact the client’s cash flow and overall financial stability.
Impact on Balance Sheet: Recourse factoring may affect the client’s balance sheet since the outstanding invoices are often considered liabilities. This can impact financial ratios and may have implications for the client’s ability to secure additional financing.
Potential Strain on Relationships: The need to enforce recourse provisions and collect outstanding debts may strain relationships between the client and their customers. This is especially true if the client has to take legal action to recover payments.
Limited Risk Transfer: While the factor assumes the risk of non-payment initially, the recourse provision means that this risk is eventually transferred back to the client. This limited risk transfer may not provide the same level of security as non-recourse factoring.
Higher Advance Rates Come at a Cost: While recourse factoring may offer higher advance rates compared to non-recourse factoring, these higher advances often come with higher fees and costs. Clients should carefully consider the overall cost of financing.
Potential for Higher Interest Rates: The factor may charge higher interest rates on the amounts advanced in recourse factoring due to the higher level of risk involved. This can increase the overall cost of financing for the client.
Impact on Reputation: Enforcing recourse provisions and collecting debts may have a negative impact on the client’s reputation, especially if these actions become visible to customers. This can affect customer trust and loyalty.
Difference Between Recourse and Non-Recourse Factoring
Here’s a table highlighting the key differences between recourse and non-recourse factoring:
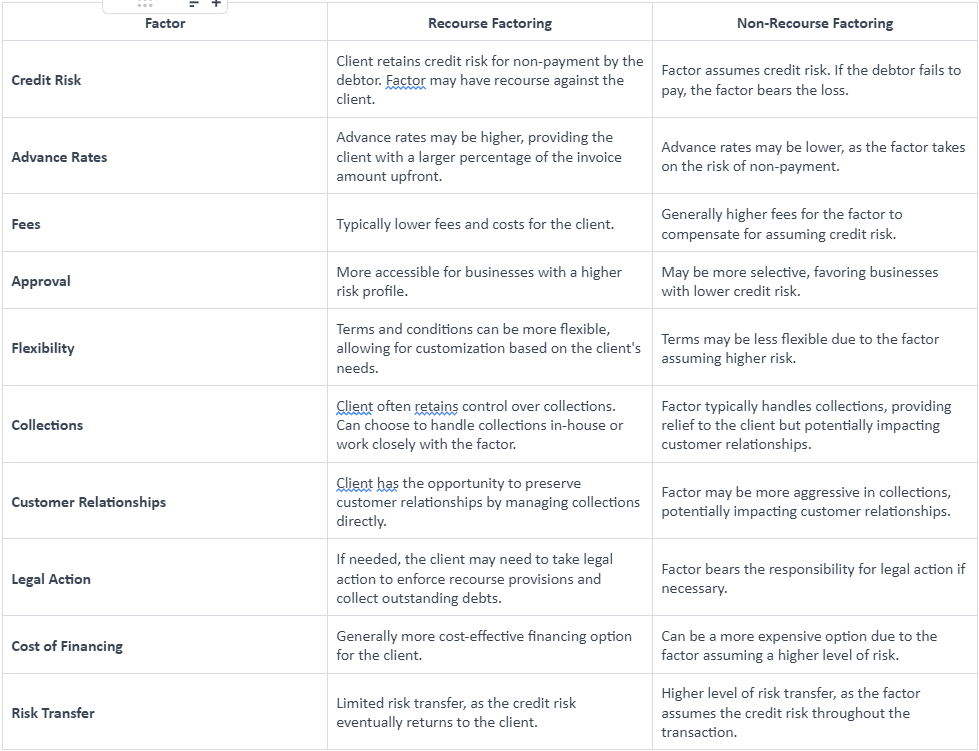
Final Note
Recourse Factoring emerges as a dynamic financial strategy offering businesses a unique blend of flexibility and control. By unlocking immediate cash flow through accounts receivable, companies can navigate the delicate balance between liquidity and risk management. The strategic advantage lies in higher advance rates, cost-effectiveness, and the ability to tailor solutions.
While it empowers businesses, the caveat of credit risk retention should be carefully considered. Join us on this exploration of Recourse Factoring as it reshapes the landscape of modern financing, providing a strategic lifeline for diverse business needs.
Also Read: How Factoring Benefits Manufacturers and Exporters in Apparel Industry[/vc_column_text][vc_empty_space height=””][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/3″ offset=”vc_hidden-sm vc_hidden-xs” el_class=”post-col” css=”.vc_custom_1638872146414{padding-left: 50px !important;}”][vc_widget_sidebar sidebar_id=”consulting-right-sidebar” el_id=”single-right-siebar”][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text][/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row css=”.vc_custom_1638349264629{padding-top: 100px !important;padding-bottom: 80px !important;}”][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”Related Post” font_container=”tag:h2|font_size:25px|text_align:center|color:%233c3c3c” google_fonts=”font_family:Poppins%3A300%2Cregular%2C500%2C600%2C700|font_style:600%20semi-bold%3A600%3Anormal” css=”.vc_custom_1638774169659{margin-bottom: 30px !important;}”][vc_raw_html]JTVCc21hcnRfcG9zdF9zaG93JTIwaWQlM0QlMjIxMDAwNSUyMiU1RA==[/vc_raw_html][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]