[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text][/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row el_class=”padding-sm-bottom-40″][vc_column offset=”vc_col-lg-8 vc_col-md-8″ el_class=”post-details-sec”][vc_single_image image=”12451″ img_size=”full” css=”.vc_custom_1711433623680{margin-bottom: 44px !important;}”][vc_row_inner css=”.vc_custom_1608297138483{margin-bottom: 0px !important;}”][vc_column_inner][vc_column_text]The Bill of Lading (BOL) and the Waybill are both essential documents in the realm of shipping and logistics, serving as crucial tools for documenting and tracking cargo during transportation. While they share similar purposes, there are significant differences between the two.
A Bill of Lading is a legal document issued by a carrier to the shipper, detailing the type, quantity, and destination of goods being transported. It serves as a receipt of goods, evidence of the contract of carriage, and a document of title. Essentially, it transfers ownership of the goods from the shipper to the recipient upon delivery.
On the other hand, a Waybill is a simpler document that serves as a receipt for the goods and contains instructions for their handling and delivery. Unlike the Bill of Lading, a Waybill does not confer ownership of the goods and is not negotiable. It primarily functions as a shipping label and a tracking document for carriers and consignees.
Understanding the distinctions between these documents is crucial for ensuring the smooth and efficient movement of goods in the logistics chain.
What is a Bill of Lading?
A Bill of Lading (BOL) is a legal document issued by a carrier to the shipper, acknowledging receipt of goods for shipment. It serves multiple purposes throughout the shipping process. Primarily, it acts as a contract of carriage between the shipper and the carrier, outlining the terms and conditions of transportation, including the type, quantity, and destination of the goods.
Moreover, a Bill of Lading serves as a receipt for the goods, confirming that they have been loaded onto the carrier’s vessel or transport vehicle. It also functions as a document of title, meaning it can be transferred to another party, thereby transferring ownership of the goods described in the Bill of Lading.
In international trade, the Bill of Lading plays a crucial role in facilitating the movement of goods across borders. It serves as a key document for customs clearance, providing essential information about the cargo to authorities. Additionally, it can be used for trade financing purposes, as it represents the goods’ value and can be endorsed to a third party as collateral for a loan or payment.
Overall, the Bill of Lading is a fundamental document in the logistics and shipping industry, ensuring transparency, accountability, and legal protection for all parties involved in the transportation of goods.
Also Read: What is Bill of Lading in Shipping and Exports?
Types of Bill of Lading
There are two main types of bills of lading:
Negotiable Bill of Lading: This type allows for the transfer of legal ownership of the cargo from the original holder of the bill of lading to a third party. This transfer typically occurs through a consignment arrangement, wherein the title of goods is shifted from the consignor (the seller) to the consignee (the buyer). The consignee, acting as a third party, assumes financial responsibility and gains legal ownership of the goods.
Non-Negotiable Bill of Lading: In contrast, with this type, the consignee is specifically named when the bill is initially issued and cannot be altered afterwards. Consequently, neither the shipper nor the consignee can transfer legal title and ownership of the cargo to a third party by endorsing the bill.
Also Read: Exploring the Diverse Types of Bill of Lading in Shipping
What is a Waybill?
A Waybill is a document used in the transportation of goods, serving as a receipt and an essential record of the shipment. Unlike a Bill of Lading, which is a legally binding document and can serve as a title for the goods, a Waybill is more of a simplified version that primarily acts as a receipt and provides instructions for handling and delivery.
Key features of a Waybill include:
Receipt for Goods: The Waybill serves as a receipt issued by the carrier or transportation company to the shipper, acknowledging that the goods have been received for shipment.
Instructions for Handling and Delivery: It contains essential instructions for the carrier regarding the handling, routing, and delivery of the goods to their destination. This includes details such as the origin and destination addresses, the consignee’s information, and any special handling requirements.
Tracking Document: The Waybill often includes a unique identification number or barcode that allows for tracking and tracing of the shipment’s progress throughout the transportation process.
Non-Negotiable: Unlike a Bill of Lading, a Waybill is typically non-negotiable and cannot be transferred to another party. It does not confer ownership of the goods and is primarily used for administrative purposes within the transportation chain.
Overall, a Waybill is a critical document in logistics and shipping, providing essential information for the transportation of goods while serving as a record of the transaction between the shipper and the carrier. It helps ensure that shipments are handled and delivered accurately and efficiently to their intended destination.
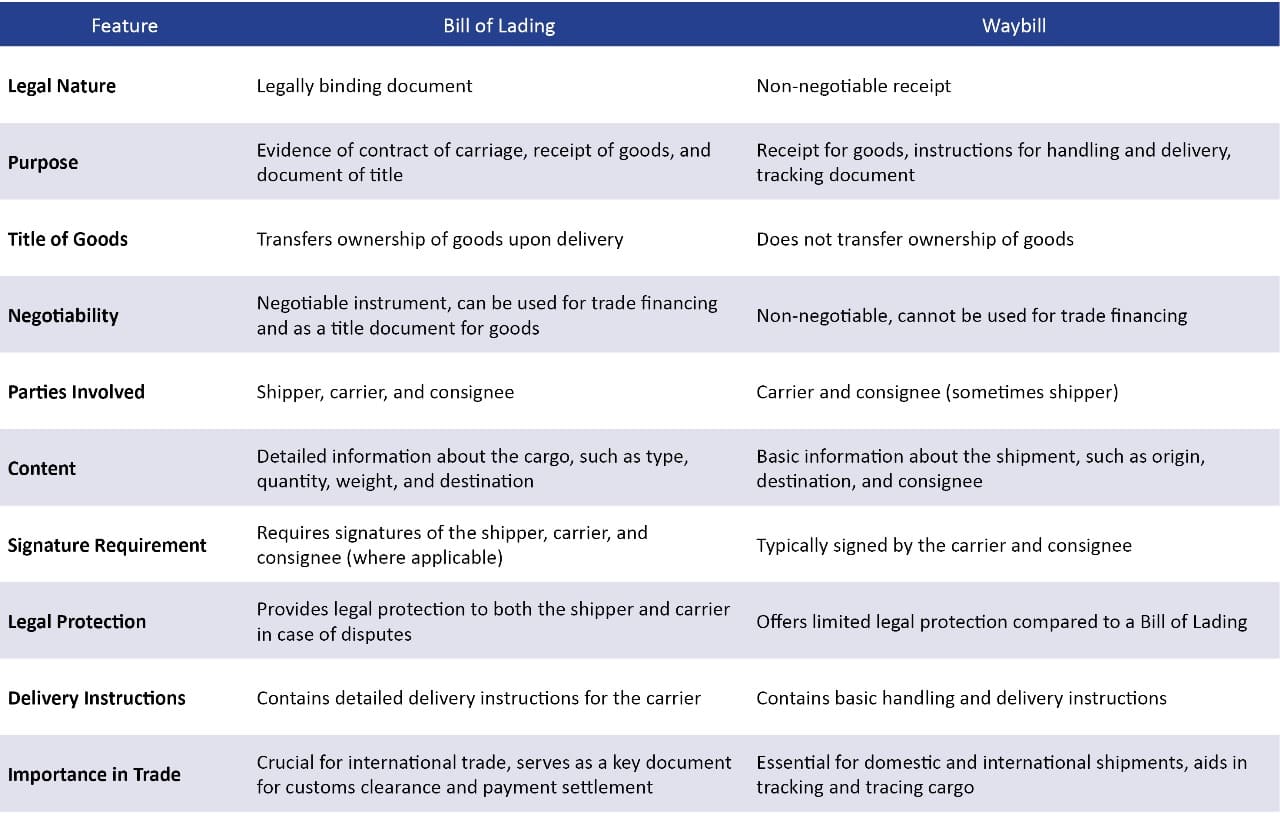
Comparison of the Bill of Lading and the Waybill
The table below illustrates the key differences between the Bill of Lading and the Waybill, highlighting their distinct purposes, legal implications, and roles in the shipping and logistics industry.
Information Included in Waybills and Bills of Lading
Both waybills and bills of lading contain a comprehensive set of information crucial for the transportation of goods. Despite serving different purposes, they share common data points which include:
- Sender’s name, address, and contact details
- Carrier’s name, address, contact details, and identification number
- Recipient’s name, address, and contact information
- Loading and unloading locations (ports or airports)
- Vessel or vehicle identification details
- Dates of shipment
- Detailed description and condition of the goods
- Quantity and dimensions of the cargo
- Payment details
- Contract terms
- Special handling instructions
These documents ensure smooth coordination between parties involved in the shipping process and provide essential information for tracking and handling the shipment efficiently.
Final Words
In conclusion, while both the Bill of Lading and the Waybill are vital documents in the realm of shipping and logistics, they serve distinct purposes and possess unique characteristics.
The Bill of Lading acts as a legally binding document, serving as evidence of the contract of carriage, a receipt for goods, and a document of title. It facilitates the transfer of ownership of goods and plays a crucial role in international trade, providing essential information for customs clearance and trade financing.
On the other hand, the Waybill is a simpler document that primarily serves as a receipt for the goods and provides instructions for their handling and delivery. It is non-negotiable and does not confer ownership of the goods but is indispensable for tracking and tracing shipments throughout the transportation process.
Understanding the differences between these documents is essential for ensuring efficient and transparent movement of goods in the logistics chain, providing legal protection and facilitating smooth transactions between parties involved in the shipping process.
Also Read: What Is a Straight Bill of Lading?[/vc_column_text][vc_empty_space height=””][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/3″ offset=”vc_hidden-sm vc_hidden-xs” el_class=”post-col” css=”.vc_custom_1638872146414{padding-left: 50px !important;}”][vc_widget_sidebar sidebar_id=”consulting-right-sidebar” el_id=”single-right-siebar”][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text][/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row css=”.vc_custom_1638349264629{padding-top: 100px !important;padding-bottom: 80px !important;}”][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”Related Post” font_container=”tag:h2|font_size:25px|text_align:center|color:%233c3c3c” google_fonts=”font_family:Poppins%3A300%2Cregular%2C500%2C600%2C700|font_style:600%20semi-bold%3A600%3Anormal” css=”.vc_custom_1638774169659{margin-bottom: 30px !important;}”][vc_raw_html]JTVCc21hcnRfcG9zdF9zaG93JTIwaWQlM0QlMjIxMDAwNSUyMiU1RA==[/vc_raw_html][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]