[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text][/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row el_class=”padding-sm-bottom-40″][vc_column offset=”vc_col-lg-8 vc_col-md-8″ el_class=”post-details-sec”][vc_single_image image=”12144″ img_size=”full” css=”.vc_custom_1708413859503{margin-bottom: 44px !important;}”][vc_row_inner css=”.vc_custom_1608297138483{margin-bottom: 0px !important;}”][vc_column_inner][vc_column_text]Financial resources are the lifeblood of business growth, and this holds particularly true in the context of global commerce. As businesses set their sights on new horizons, they inevitably confront monetary challenges. Whether it’s entering new markets or navigating international transactions, the need for sufficient funds becomes paramount. In this dynamic landscape, the ability to secure and manage finances effectively becomes a cornerstone for success, allowing businesses to not only survive but thrive in the competitive world of global trade.
There are two main ways they try to solve these challenges: export factoring and traditional financing.
This blog will talk about how these two are different and how they help businesses that want to sell things in other countries. Let’s keep it simple and see what makes them special for exporters.
What is Export Factoring?
Export factoring is a financial practice crucial for international trade. It involves a third-party financial entity, known as a factor, stepping in to facilitate the sale between an exporter and a foreign buyer. The exporter sells its unpaid invoices to the factor at a discount, gaining immediate funds, while the factor takes on the responsibility of collecting payment from the buyer.
This process enhances cash flow, mitigates risks associated with delayed payments, and fosters a secure and efficient global trade environment for businesses navigating cross-border transactions.
Also Read: 9 Ways Export Factoring Reduces Risk and Boosts Your Bottom Line
What is Traditional Financing?
Traditional financing refers to conventional methods of obtaining funds for business activities. It typically involves securing loans or credit from banks or financial institutions. In traditional financing, businesses borrow a specific amount, agree upon repayment terms, and often provide collateral.
This form of financing has been a longstanding approach for companies to fund various operations, expansions, or capital expenditures. Unlike alternative methods, traditional financing is characterized by its adherence to established financial structures and practices within the conventional banking system.
Export Factoring vs. Traditional Financing
Let’s elaborate on the differences between Export Factoring and Traditional Financing:
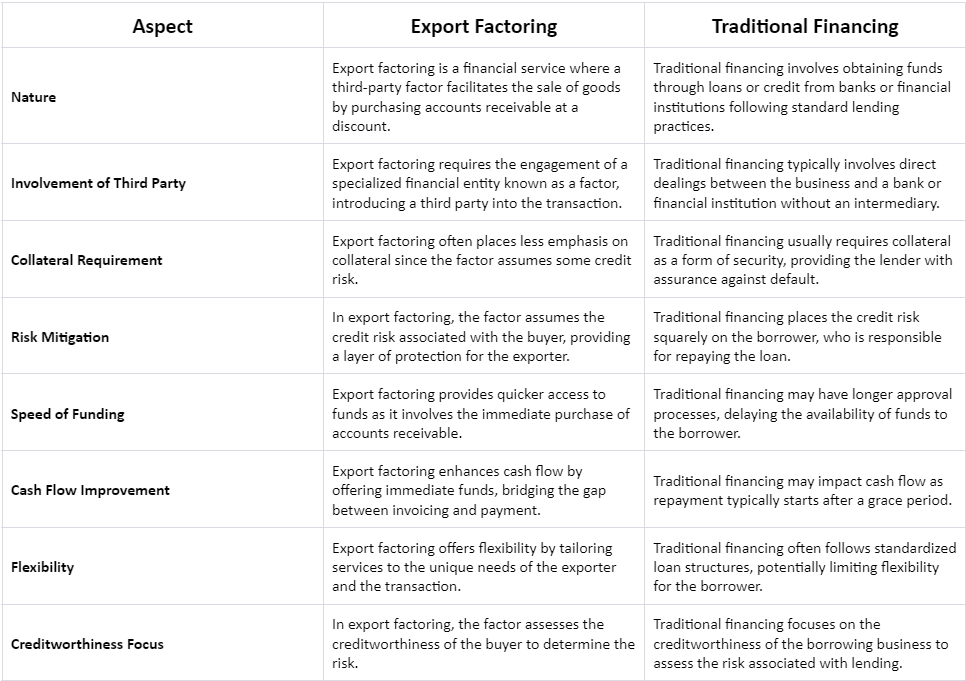
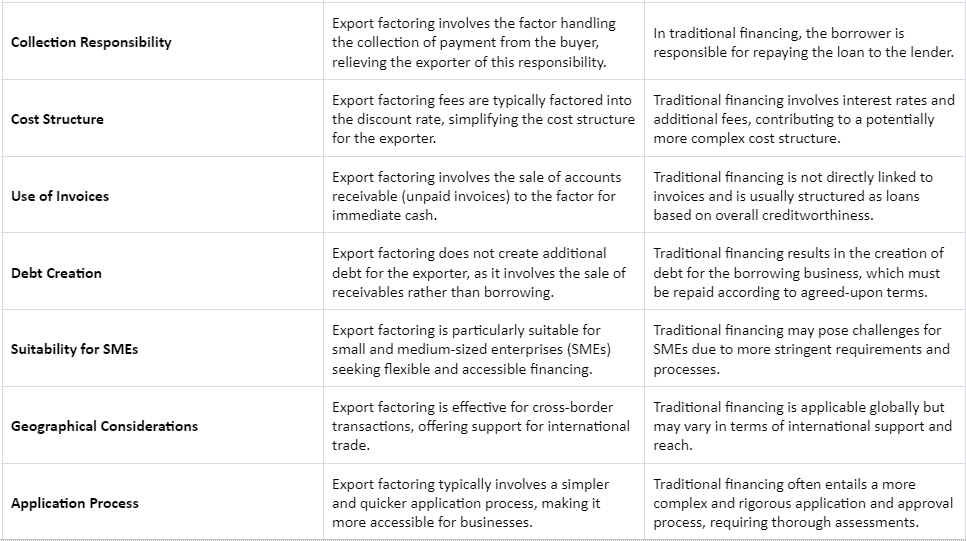
These distinctions provide businesses with a comprehensive understanding of the nuances between export factoring and traditional financing, assisting them in making informed decisions based on their specific needs and circumstances in the realm of international trade.
Factors to Consider While Choosing Export Factoring Or Traditional Financing
When deciding between export factoring and traditional financing for your business, several key factors should be carefully considered to ensure the chosen method aligns with your unique needs and objectives. Here are essential considerations for making an informed decision:
Cash Flow Needs
-
- Export Factoring:
Ideal for businesses seeking immediate cash flow improvement by converting accounts receivable into instant funds.
-
- Traditional Financing:
Suited for those with a more predictable cash flow who can afford a longer repayment period.
Credit Risk Tolerance
-
- Export Factoring:
Appeals to businesses looking to transfer credit risk to the factor, providing protection against buyer insolvency.
-
- Traditional Financing:
Suitable for businesses comfortable bearing their own credit risk and managing repayments independently.
Flexibility
-
- Export Factoring:
Offers flexibility in adapting to the specific needs of each transaction, supporting businesses with varying requirements.
-
- Traditional Financing:
May have less flexibility due to standardized loan structures, potentially limiting adaptability.
Collateral Availability
-
- Export Factoring:
Requires less emphasis on collateral, making it accessible for businesses with limited assets.
-
- Traditional Financing:
Often demands collateral as security, which may be challenging for businesses with fewer assets.
Transaction Size and Frequency
-
- Export Factoring:
Suited for businesses engaged in frequent and smaller transactions, providing a scalable financing solution.
-
- Traditional Financing:
May be more suitable for larger, less frequent transactions due to the structured nature of loans.
Geographical Considerations
-
- Export Factoring:
Effective for businesses engaged in cross-border trade, offering support for international transactions.
-
- Traditional Financing:
Applicable globally, but the level of international support may vary among financial institutions.
Cost Structure
-
- Export Factoring:
Costs, including fees, are often integrated into the discount rate, simplifying the overall cost structure.
-
- Traditional Financing:
Involves interest rates and additional fees, contributing to a potentially more complex cost structure.
Creditworthiness Assessment
-
- Export Factoring:
Focuses on the creditworthiness of the buyer, as the factor assumes the credit risk associated with the transaction.
-
- Traditional Financing:
Assesses the creditworthiness of the borrowing business, influencing the terms and conditions of the loan.
Application Process
-
- Export Factoring:
Generally features a simpler and quicker application process, making it more accessible for businesses with immediate needs.
-
- Traditional Financing:
May involve a more rigorous application and approval process, requiring comprehensive assessments.
Debt Creation
-
- Export Factoring:
Does not create additional debt for the exporter, as it involves the sale of accounts receivable.
-
- Traditional Financing:
Results in the creation of debt, requiring repayment according to agreed-upon terms.
Suitability for SMEs
-
- Export Factoring:
Particularly suitable for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) seeking accessible and flexible financing.
-
- Traditional Financing:
May pose challenges for SMEs due to more stringent requirements and processes.
By carefully evaluating these factors, businesses can make an informed choice between export factoring and traditional financing, aligning their financial strategy with their specific business goals and circumstances.
Which One is Better
Determining which financing method is better, export factoring or traditional financing, depends on the unique needs and circumstances of a business. Export factoring is advantageous for those requiring quick cash flow, prefer risk transfer to factors, and engage in frequent international transactions. On the other hand, traditional financing suits businesses with predictable cash flow, higher risk tolerance, and larger, less frequent transactions.
Evaluating factors like flexibility, collateral availability, and geographical considerations is essential to make an informed decision, ensuring the selected method aligns seamlessly with the business’s financial goals and operational requirements in the global trade landscape.
Also Read: Best Interest rate Calculator for Export Financing Trade
[/vc_column_text][vc_empty_space height=””][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/3″ offset=”vc_hidden-sm vc_hidden-xs” el_class=”post-col” css=”.vc_custom_1638872146414{padding-left: 50px !important;}”][vc_widget_sidebar sidebar_id=”consulting-right-sidebar” el_id=”single-right-siebar”][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text][/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row css=”.vc_custom_1638349264629{padding-top: 100px !important;padding-bottom: 80px !important;}”][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”Related Post” font_container=”tag:h2|font_size:25px|text_align:center|color:%233c3c3c” google_fonts=”font_family:Poppins%3A300%2Cregular%2C500%2C600%2C700|font_style:600%20semi-bold%3A600%3Anormal” css=”.vc_custom_1638774169659{margin-bottom: 30px !important;}”][vc_raw_html]JTVCc21hcnRfcG9zdF9zaG93JTIwaWQlM0QlMjIxMDAwNSUyMiU1RA==[/vc_raw_html][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]