- December 3, 2024
- Posted by: admin
- Categories: Export Financing, Blog

In today’s globalized economy, businesses frequently source goods from international markets to access cost-effective supplies and maintain their competitive edge. However, this often comes with challenges, especially for small businesses that may face cash flow constraints while waiting for their shipments to arrive. Import financing serves as a crucial tool to bridge this financial gap, enabling businesses to thrive in global trade.
This article dives into the meaning, uses, techniques, and advantages of import financing, providing insights into how it works and why it is essential for businesses.
What Is Import Financing?
Import financing refers to a range of financial solutions designed to help businesses fund the purchase of goods from overseas suppliers. These solutions allow businesses to maintain cash flow for ongoing operations while meeting future demand through international purchases.
By using import financing, businesses can manage their short-term cash requirements effectively, reducing risks and ensuring smooth operations. It is a vital tool for companies that want to scale their operations without compromising their financial stability.
An Example of Import Financing in Action
Consider Company A, a steel goods manufacturer in the United States, planning to import raw materials from Company B in China. Company A lacks the funds to pay upfront for the steel and opts for import financing.
By utilizing buyer’s credit from the Export-Import (EXIM) Bank of China, Company A can pay Company B upon delivery of the steel. This immediate payment not only strengthens their relationship with Company B but also allows them to negotiate better pricing. Once the manufactured goods are sold, Company A repays the EXIM Bank.
This example highlights how import financing supports businesses by enabling smoother transactions and fostering growth opportunities.
Key Uses of Import Financing
Import financing is more than just a cash flow solution; it addresses several other business needs:
- Optimizing Cash Flows: Ensures businesses can continue daily operations without financial interruptions.
- Risk Management: Helps businesses hedge against risks like currency fluctuations and supplier defaults.
- Working Capital Support: Provides flexibility in managing funds required for inventory purchases.
- Supplier Relationships: Timely payments improve supplier trust and result in long-term partnerships.
- Supply Chain Efficiency: Facilitates faster procurement, ensuring minimal disruptions in operations.
In the U.S., import financing is increasingly vital, with international trade financing reaching $625.4 million in 2022, marking a 5.1% increase from the previous year.
Parties Involved in Import Financing
Several entities contribute to the smooth execution of import financing:
- Banks: Provide letters of credit, guarantees, and other financial instruments.
- Trade Finance Companies: Offer specialized funding solutions tailored to international trade.
- Importers and Exporters: The primary participants in any trade transaction.
- Insurers: Mitigate risks related to goods in transit.
- Export Credit Agencies: Reduce financial risks for exporters by providing guarantees and insurance.
These entities collectively ensure that international trade processes are efficient, secure, and mutually beneficial.
Popular Import Financing Techniques
Import financing techniques provide businesses with flexible options to manage cash flows and support international trade transactions. Below are some of the most commonly used methods, their advantages, and their suitability for different business needs:
1. Inventory Financing
This involves securing a loan or line of credit using inventory as collateral. Businesses can use this method to purchase goods that are not intended for immediate sale, such as seasonal inventory or bulk raw materials.
Key Benefits:
- Provides quick access to funds.
- Ideal for businesses with limited credit history.
2. Letters of Credit (LCs)
An LC is a financial guarantee provided by the importer’s bank to the exporter. It ensures the exporter receives payment once all agreed terms are met, making it a highly secure method for international trade.
Types of LCs:
- Revolving LCs: Allow repeated transactions under a single agreement.
- Non-Revolving LCs: Used for one-time payments.
Advantages:
- Builds trust between buyers and suppliers.
- Reduces payment risks.
3. Supply Chain Finance (SCF)
In SCF, a third party finances the supplier on behalf of the buyer, ensuring the supplier gets paid faster. The buyer then repays the third party at a later date, offering flexibility to both parties.
Best For: Businesses seeking to improve supplier relationships and cash flow efficiency.
4. Purchase Order (PO) Financing
This method enables businesses to obtain funding for confirmed purchase orders. A third-party financier pays the supplier, and the business repays once the goods are sold.
Benefits:
- Doesn’t rely on credit history.
- Useful for businesses with fluctuating cash flow.
5. Bank Guarantees
A bank guarantee assures the exporter of payment in case the importer defaults. This method is often used for high-value transactions or when trust between parties is still building.
Drawback: Higher costs and stringent eligibility requirements.
6. Buyer’s Credit
This allows importers to obtain loans from overseas lenders, often in the exporter’s country, at competitive interest rates. It’s a popular choice for large-scale transactions.
Advantages:
- Cheaper funding options.
- Offers longer repayment periods.
7. Invoice Factoring
Businesses sell their unpaid invoices to a factoring company in exchange for immediate cash. This method is suitable for importers with numerous pending invoices.
Benefits:
- Provides quick liquidity.
- Reduces administrative burden.
8. Forfaiting
Forfaiting involves selling long-term receivables to a third party. This technique is particularly useful for capital goods transactions or agreements with extended payment terms.
Advantages:
- Reduces credit risk for the exporter.
- Ensures immediate cash flow for importers.
Choosing the Right Technique
Each technique has its own set of benefits and is suitable for specific business scenarios. For instance:
- LCs are ideal for risk-averse businesses.
- Inventory financing works well for seasonal goods.
- Buyer’s credit is best for large imports with long repayment timelines.
By evaluating their financial needs and transaction scale, businesses can select the most appropriate import financing method to streamline operations, reduce risks, and strengthen supplier relationships.
Comparing Short-Term and Long-Term Import Financing
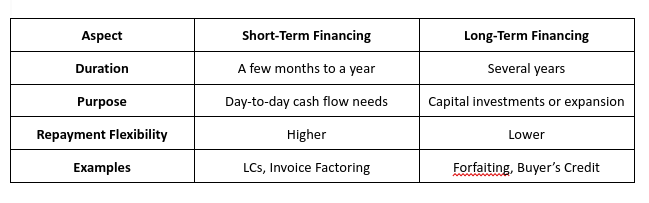
Businesses should choose financing based on their specific needs, ensuring alignment with their cash flow and operational goals.
Benefits of Import Financing
Import financing offers businesses a range of solutions to manage cash flow, mitigate risks, and facilitate smooth international trade transactions. Here are the key advantages:
Improved Cash Flow:
Import financing methods, like supply chain finance and purchase order financing, provide immediate funds to cover purchase costs. This allows businesses to operate without depleting working capital, ensuring smoother operations.
Risk Mitigation:
Techniques like letters of credit and bank guarantees reduce risks for both buyers and sellers by ensuring timely payments and product delivery. These methods build trust in international transactions.
Increased Purchasing Power:
Financing options such as buyer’s credit and inventory financing enable businesses to place larger orders or buy in bulk, often leading to discounts and cost savings.
Faster Transactions:
Tools like invoice factoring and supply chain finance streamline payment processes, allowing importers to receive goods faster while suppliers get paid promptly.
Flexible Repayment Options:
Many import financing solutions offer extended repayment terms, giving businesses more time to generate revenue before settling debts.
In essence, import financing ensures operational efficiency, reduces financial strain, and strengthens supplier relationships, making it an essential tool for global trade success.
FAQs on Import Financing
Q1. Who provides import financing?
Banks, trade finance companies, and export credit agencies.
Q2. What documents are required?
Purchase orders, invoices, shipping documents, and insurance certificates.
Q3. How does LC differ from Documentary Collection?
An LC guarantees payment, while Documentary Collection releases shipping documents only upon payment.
Conclusion
Import financing is an indispensable tool for businesses engaged in international trade. By providing the necessary funds to procure goods, it ensures smooth operations, strengthens supplier relationships, and enables business growth.
From inventory financing to buyer’s credit, the diverse methods available cater to varying needs, helping businesses thrive in a competitive global marketplace. With careful evaluation of options and proper planning, businesses can leverage import financing to minimize risks, optimize cash flows, and achieve sustained growth.
Also Read: