Ever wondered how your latest online purchase made its way from a faraway factory to your doorstep? Well, let’s shine a light on the unsung hero of the logistics world: the Inland Container Depot (ICD)! Don’t worry, despite the fancy name, ICDs are simple concepts for goods on their journey from port to your local store.
In this blog post, we’re understanding the world of ICDs—no complicated jargon or confusing diagrams, just a simple and enjoyable exploration of what they are, why they matter, and how they work. So, let’s dive into the fascinating world of Inland Container Depots!
What’s an Inland Container Depot (ICD)?
Inland Container Depots (ICDs) are specialized facilities strategically located inland, typically near major transportation hubs like ports, rail terminals, or airports. They serve as key nodes in the transportation network, facilitating the efficient movement of cargo containers between seaports and inland destinations.
ICDs provide various services essential for the smooth flow of goods, including container handling, storage, customs clearance, and consolidation. They act as intermediate points where cargo containers are transferred between different modes of transport, such as ships, trucks, and trains.
These facilities play a vital role in reducing congestion at seaports, enhancing supply chain efficiency, and lowering transportation costs. By providing centralized facilities for cargo handling and customs clearance, ICDs contribute to streamlining international trade and improving overall logistics operations.
Role of Inland Container Depots (ICDs) in Global Logistics
Inland Container Depots (ICDs) play an important role in the global logistics chain by providing vital storage and handling facilities for shipping containers. Situated in the hinterlands, away from major ports, these depots serve as essential nodes for the storage, consolidation, and movement of cargo containers.
Often dubbed as “Dry Ports” due to their inland location, ICDs act as intermediaries between seaports and inland destinations. Shipping companies utilize these facilities to store and manage containers before and after their transportation to and from seaports.
Beyond storage, ICDs offer a range of services including container handling, customs clearance, and cargo consolidation. By providing centralized facilities for these operations, ICDs contribute significantly to streamlining international trade, reducing congestion at seaports, and enhancing overall supply chain efficiency.
Importance of Inland Container Depots (ICDs)
At an Inland Container Depot (ICD), a diverse array of professionals, including sea custodians, freight forwarders, customs brokers, and customs department officials, converge to offer their services to importers and exporters. Positioned closer to importers’ and exporters’ facilities rather than distant ports, ICDs streamline the shipment processing right at their doorsteps, ensuring convenience and efficiency.
By providing services in close proximity to warehouses and factories, ICDs alleviate the burden on distant ports, which often face constraints on storage space due to land-use regulations. This decentralization helps to reduce stress and congestion at ports, ensuring smoother and more efficient logistics operations.
Functions of Inland Container Depots (ICDs)
Inland Container Depots (ICDs) serve as crucial hubs in the logistics chain, offering a range of functions to streamline the movement of cargo containers and facilitate international trade. Here’s a breakdown of their key roles:
Temporary Storage: ICDs function as temporary warehouses for cargo containers, providing a stopover point for containers before they are transported to the port for loading onto ships. This allows for efficient inventory management and ensures the timely delivery of goods.
Cargo Consolidation: Exporters can utilize ICDs to consolidate their cargo inside containers before shipping. This helps optimize container space and minimize transportation costs by ensuring that containers are fully utilized.
Customs Clearance: ICDs offer export and import customs clearance services, allowing for the smooth processing of shipments. This includes document verification, duty assessment, and compliance with customs regulations. By providing these services on-site, ICDs streamline the clearance process and reduce delays.
Servicing and Repair: In addition to storage and customs clearance, ICDs also serve as servicing and repair facilities for containers and other equipment used in the transportation process. This ensures that containers are in optimal condition for shipping, minimizing the risk of damage or delays during transit.
Overall, ICDs play a vital role in facilitating trade by providing essential infrastructure and services to importers, exporters, and logistics providers. From storage to customs clearance and maintenance, these facilities help ensure the smooth flow of goods through the supply chain, contributing to the efficiency and reliability of international trade operations.
Benefits of Inland Container Depots (ICDs)
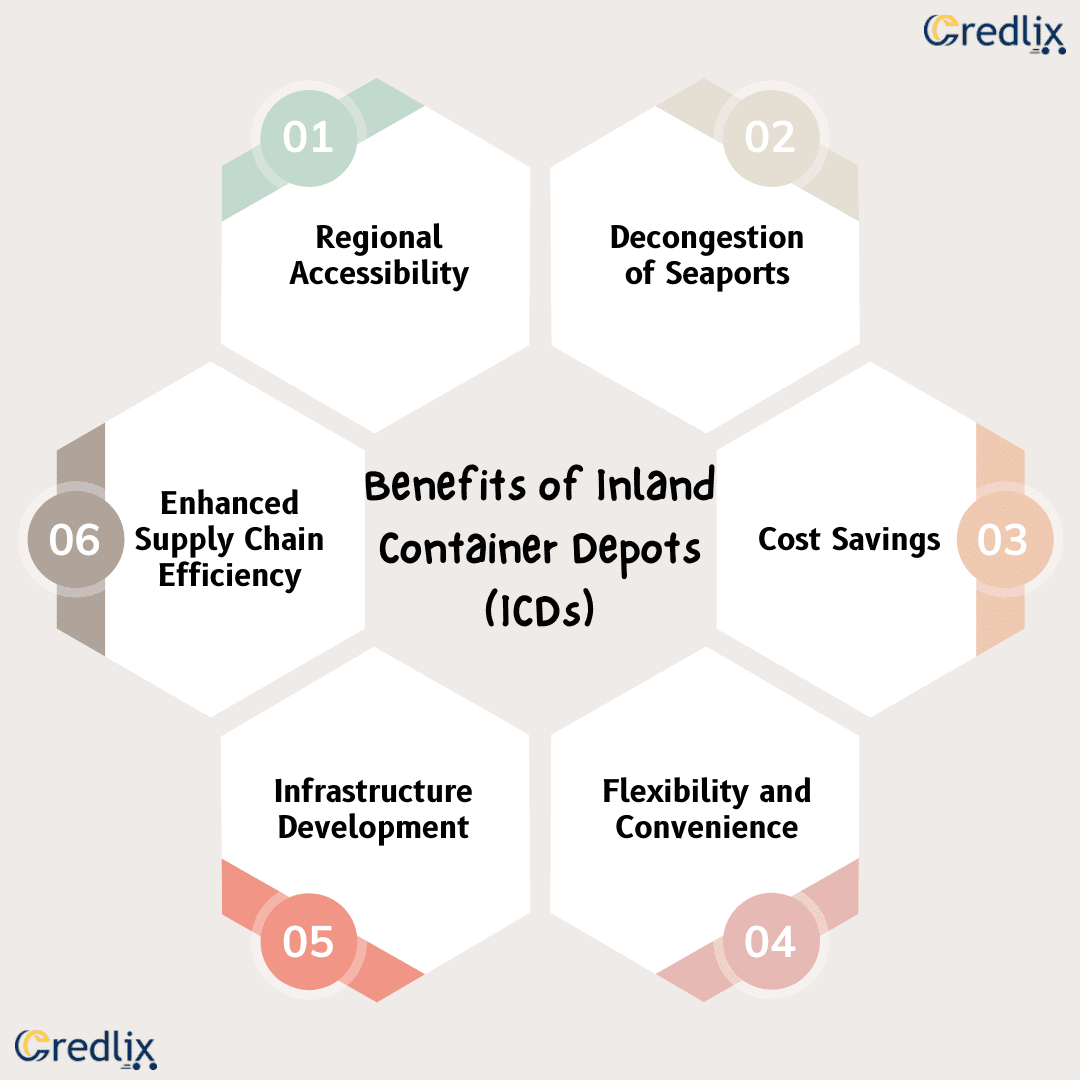
Inland Container Depots (ICDs) offer a host of advantages that contribute to the efficiency and effectiveness of the logistics chain. Here are some key benefits:
Regional Accessibility
ICDs are strategically located in inland regions, making them easily accessible to businesses located away from seaports. This proximity reduces transportation costs and transit times for goods, particularly for industries located far from coastal areas.
Decongestion of Seaports
By providing storage and handling facilities for cargo containers inland, ICDs help alleviate congestion at seaports. This reduces wait times for ships, trucks, and other transportation modes, resulting in smoother operations and improved turnaround times.
Cost Savings
Utilizing ICDs can lead to significant cost savings for businesses involved in international trade. By consolidating cargo and providing value-added services such as customs clearance and container maintenance, ICDs help streamline operations and reduce overall logistics expenses.
Flexibility and Convenience
ICDs offer flexibility in cargo handling and storage, allowing businesses to efficiently manage their inventory and distribution networks. Additionally, the availability of customs clearance services at ICDs enhances convenience for importers and exporters, eliminating the need to travel to distant ports for clearance procedures.
Infrastructure Development
The establishment of ICDs stimulates infrastructure development in inland regions, including transportation networks and supporting facilities. This can lead to economic growth and job creation in surrounding areas, contributing to regional development and prosperity.
Enhanced Supply Chain Efficiency
By acting as key nodes in the logistics network, ICDs improve supply chain efficiency by optimizing the movement of goods between ports and inland destinations. This results in faster delivery times, improved inventory management, and better overall performance for businesses engaged in global trade.
Disadvantages of Inland Container Depots (ICDs)
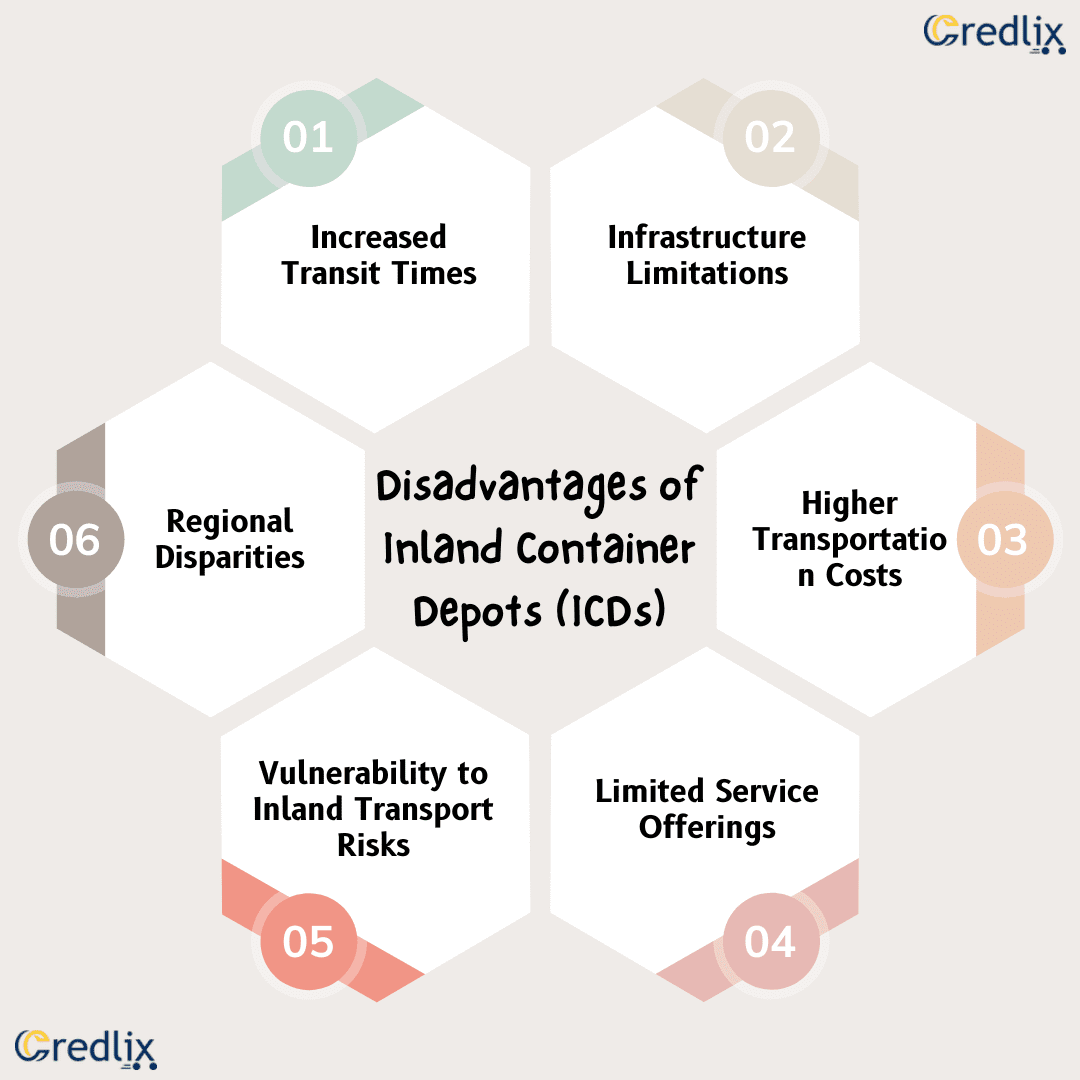
While Inland Container Depots (ICDs) offer numerous advantages, there are also some drawbacks to consider:
Increased Transit Times
Transporting cargo containers to and from inland depots adds an additional leg to the transportation process, which can result in longer transit times compared to direct shipments to seaports. This may lead to delays in delivery schedules and increased inventory holding costs for businesses.
Infrastructure Limitations
Inland regions may lack the necessary infrastructure to support large-scale container handling operations, leading to limitations in capacity and efficiency at ICDs. This could result in congestion, bottlenecks, and operational challenges for businesses relying on these facilities.
Higher Transportation Costs
While ICDs offer cost-saving benefits in terms of storage and handling, the additional transportation costs incurred in moving containers between ports and inland depots may offset some of these savings. Businesses must carefully evaluate the overall logistics costs associated with utilizing ICDs.
Limited Service Offerings
Inland depots may not offer the full range of services available at seaports, particularly in terms of specialized handling equipment, customs facilities, and international trade services. This could result in additional complexities and requirements for businesses using ICDs for their shipments.
Vulnerability to Inland Transport Risks
Cargo transported to and from ICDs via road or rail may be more susceptible to risks such as accidents, theft, and disruptions in transportation networks. This could pose challenges for businesses in terms of security, insurance costs, and supply chain resilience.
Regional Disparities
The location of ICDs in specific inland regions may exacerbate regional disparities in economic development and access to trade opportunities. Businesses located farther from ICDs may face higher transportation costs and logistical challenges compared to those in closer proximity.
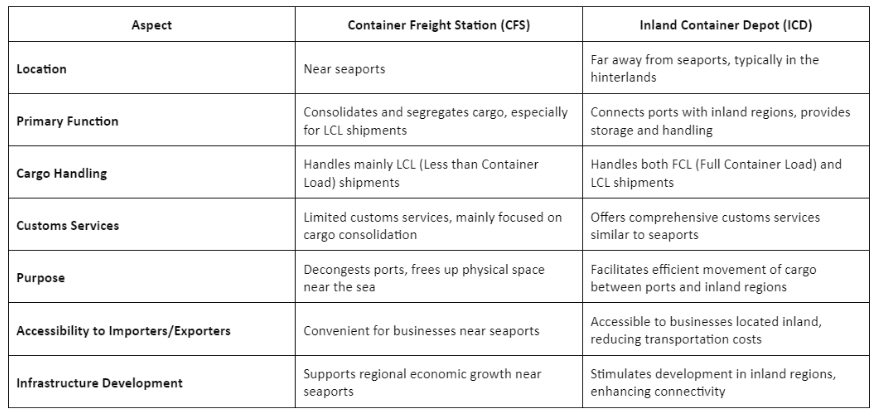
D/B Container Freight Station (CFS) and Inland Container Depot (ICD)
The table below provides a clear comparison between Container Freight Stations (CFS) and Inland Container Depots (ICD) based on various aspects such as location, primary function, cargo handling, customs services, purpose, accessibility, and infrastructure development.
Conclusion
Inland Container Depots (ICDs) play an indispensable role in the global logistics landscape, connecting ports with inland regions and streamlining the movement of goods. Despite some drawbacks, the benefits of ICDs, including cost savings, supply chain efficiency, and regional development, underscore their significance in facilitating international trade and ensuring the smooth flow of cargo from factory to doorstep.
Also Read: LCL Shipments in Logistics and Shipping: Meaning, Costs, and More