- October 22, 2024
- Posted by: admin
- Categories: Export Financing, Blog
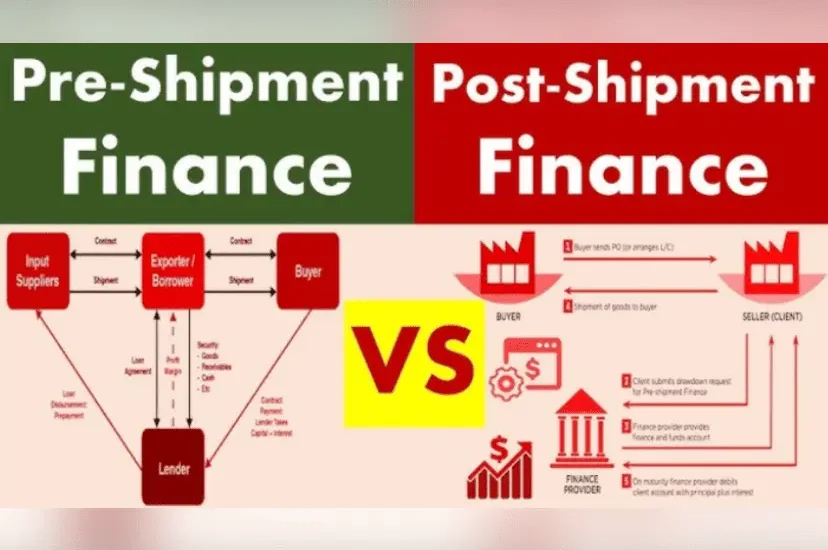
When it comes to international trade, managing cash flow is critical for exporters. They need funds not just after shipping goods but also before sending them out. This is where pre-shipment and post-shipment finance come in, offering businesses the necessary financial backing during various stages of the export process. Let’s break down what these terms mean, their differences, and how they benefit exporters.
What is Pre-Shipment Finance?
Pre-shipment finance refers to the funds extended to exporters before they ship goods. This finance helps cover the costs of producing, packaging, and preparing goods for export. From the moment an exporter receives an order until the goods are shipped, they may require working capital for things like raw materials, processing, labor, packaging, and transportation.
Financial institutions, like banks or trade finance platforms, typically provide this type of loan. It is usually available for a period of up to 270 days, depending on the confirmed export order or a Letter of Credit (LC) from the buyer. This type of credit is known as “packing credit” because it helps exporters with the funds they need to ‘pack’ or prepare goods for shipment.
Key Uses of Pre-Shipment Finance:
- Purchasing raw materials: Funds are used to acquire the necessary materials for manufacturing.
- Processing and converting materials: This includes labor costs, machinery use, and any other expenses tied to converting raw materials into finished goods.
- Packaging and warehousing: Pre-shipment finance can help cover the costs of packaging the goods securely for shipment and storing them before they are shipped.
- Transport and shipping: The funds can also be used for moving goods from the warehouse to the port of export.
- Clearing customs and excise duties: The funds are sometimes required to cover clearance charges.
- Pre-shipment inspection: The costs related to quality checks and inspections before shipment can also be met with this finance.
What is Post-Shipment Finance?
Post-shipment finance, as the name suggests, is the financial assistance provided after goods have been shipped to the buyer. Exporters often face a gap between shipping their goods and receiving payment from international buyers. This gap can be bridged by post-shipment finance, which allows exporters to maintain healthy cash flow until they receive their export proceeds.
Financial institutions usually extend post-shipment finance against shipping documents like bills of lading, which act as proof that the goods have been shipped. This type of credit generally comes at a concessional interest rate, making it affordable for exporters.
Key Features of Post-Shipment Finance:
- Short-term or medium-term loans: Most post-shipment loans are short-term, typically lasting up to 60 days. However, in some cases, they can be extended for a longer duration.
- Evidence-based: Loans are given against documents like shipping bills that confirm the shipment of goods.
- Fixed percentage: The amount of post-shipment finance is usually a fixed percentage of the export order value, helping exporters cover any immediate financial needs.
How Do Pre-Shipment and Post-Shipment Finance Differ?
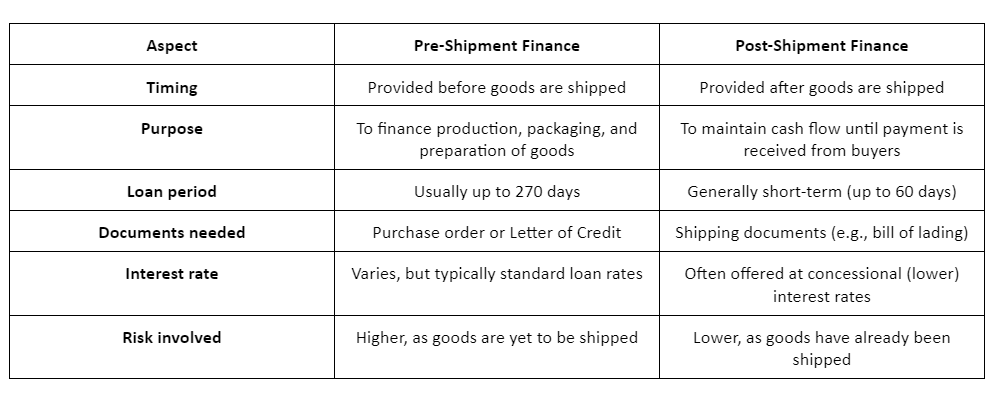
Both pre-shipment and post-shipment finance aim to support exporters, but they do so at different stages of the export process. Below is a breakdown of their differences:
Eligibility for Pre-Shipment and Post-Shipment Finance
Pre-shipment and post-shipment finance are available to all types of exporters, including:
- Merchant exporters: Businesses that purchase goods from manufacturers and sell them overseas.
- Manufacturer exporters: Companies that produce goods themselves for export.
- Export and trading houses: Large organizations that specialize in international trade.
The loans can be offered by traditional banks, non-banking financial companies (NBFCs), and trade finance platforms. Financial technology (fintech) companies have also entered this space, offering innovative financing solutions tailored to the needs of exporters.
Key Benefits of Pre-Shipment and Post-Shipment Finance
Both types of finance offer several advantages for exporters:
Improved Cash Flow:
- Pre-shipment finance provides the working capital needed to complete an order, ensuring that exporters can fulfill export contracts even if they don’t have immediate access to funds.
- Post-shipment finance bridges the gap between shipping goods and receiving payments, allowing exporters to maintain business operations smoothly.
Lower Costs:
- With concessional interest rates, exporters can finance their operations without incurring high borrowing costs.
Flexibility:
- Both pre-shipment and post-shipment finance offer flexibility in how funds can be used, whether it’s to buy raw materials or cover shipping and inspection costs.
No Collateral Needed:
- In many cases, exporters don’t need to put up collateral to secure post-shipment finance. Shipping documents like the bill of lading often serve as enough security for the loan.
Common Questions
1. Why is post-shipment finance important?
Post-shipment finance helps exporters manage their working capital during the period between shipping goods and receiving payments from foreign buyers. Without it, businesses may struggle with liquidity, especially if there are delays in payment from buyers.
2. Can pre-shipment and post-shipment finance be received in foreign currency?
Yes, financial institutions in India provide both pre-shipment and post-shipment finance in foreign currency, often in U.S. dollars. This helps exporters manage currency exchange risks.
3. What is the pre-shipment inspection process?
Pre-shipment inspection is a process where either the buyer or an inspection agency checks the goods before they are shipped. This is done to ensure that the quality and quantity of the merchandise meet the agreed-upon standards.
Also Read: What is Post-Shipment Credit Finance?
How Export Financing Has Evolved?
The concept of export financing was introduced in India by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in 1967. The goal was to provide exporters with access to short-term working capital at competitive interest rates. Over the years, banks, financial institutions, and fintech companies have developed a range of financing products to support exporters.
One of the recent trends in export finance is the emergence of digital platforms that offer trade financing solutions. These fintech platforms streamline the process of securing pre-shipment and post-shipment finance, making it easier and faster for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) to get the funds they need.
Conclusion
Pre-shipment and post-shipment finance are critical tools for exporters to manage their working capital and ensure smooth international trade operations. Pre-shipment finance provides the funds needed to produce and prepare goods for export, while post-shipment finance helps bridge the financial gap after goods have been shipped. Together, these financing options play a vital role in supporting exporters, especially small and medium-sized businesses, in the competitive global market.
Also Read: What Exporters Need to Know About Post-Shipment Credit