[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text][/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row el_class=”padding-sm-bottom-40″][vc_column offset=”vc_col-lg-8 vc_col-md-8″ el_class=”post-details-sec”][vc_single_image image=”12842″ img_size=”full” css=”.vc_custom_1715243015399{margin-bottom: 44px !important;}”][vc_row_inner css=”.vc_custom_1608297138483{margin-bottom: 0px !important;}”][vc_column_inner][vc_column_text]Do you want to know what exactly India’s Bill of Entry is all about? Especially in the GST terms? Well, it’s like a gateway for goods entering the country, marking the start of the customs clearance journey. But how does it fit into India’s GST system? Let’s break it down simply.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through India’s Bill of Entry – what it means, how payments work, and what you need to know about filing it. We’ll keep things clear, so whether you’re a seasoned importer, a newbie in the business world, or just curious about GST, this exploration of the Bill of Entry will make it all crystal clear. Ready to dive in and demystify the process? Let’s get started!
What is a Bill of Entry?
A Bill of Entry (BOE) is a vital document filed by importers or customs clearing agents upon the arrival of goods in an importing country. It serves as the official paperwork required to obtain the imported goods through the customs clearance process. Essentially, the BOE acts as a record-keeping tool for the government, documenting the flow of goods and services entering and exiting the country.
Without this document, the importation of goods would lack the necessary legal formalities, highlighting the BOE’s critical role in facilitating international trade while ensuring compliance with customs regulations.
What is the Importance of the Bill of Entry?
Following are some of the major importance of a Bill of Entry:
Legal Requirement: The Bill of Entry is a mandatory legal document required by importers or customs clearing agents for obtaining imported goods through customs clearance processes.
Facilitates Customs Clearance: It serves as the official paperwork needed to clear goods through customs, ensuring compliance with import regulations.
Records Flow of Goods: The Bill of Entry enables governments to maintain accurate records of the flow of goods entering and exiting the country.
Monitoring Trade Activities: Governments use the information recorded in the Bill of Entry to monitor and analyze trade activities, including imports and exports.
Ensures Compliance: By documenting details of imported goods, the Bill of Entry helps ensure compliance with customs regulations and trade policies.
Determines Duties and Taxes: The information provided in the Bill of Entry is used to calculate and levy applicable duties, taxes, and tariffs on imported goods.
Prevents Illegal Imports: Proper documentation through the Bill of Entry helps prevent illegal imports and smuggling by providing transparency in trade transactions.
Supports Trade Statistics: The data collected from Bill of Entry documents contributes to the compilation of trade statistics, aiding in economic analysis and policy-making.
Facilitates Trade Documentation: The Bill of Entry is an essential component of trade documentation, providing proof of legal importation for business transactions.
Promotes Transparency and Accountability: By requiring the submission of the Bill of Entry, customs authorities promote transparency and accountability in international trade, ensuring that goods are imported and cleared through legal channels.
Types of Bill of Entry
Know about the different types of Bill of Entry below:
Regular Bill of Entry: This is the standard document used for goods imported for home consumption, covering a wide range of imports subject to various customs duties and taxes.
Warehouse Bill of Entry: Used when goods are imported and stored in a customs bonded warehouse without immediate clearance for home consumption. This allows importers to defer payment of duties until the goods are removed from the warehouse.
Ex-Bond Bill of Entry: Filed when goods stored in a bonded warehouse are ready for clearance for home consumption or exportation. It facilitates the release of goods from the warehouse while fulfilling customs requirements.
High Sea Sales Bill of Entry: Required for goods sold while still in transit, typically on the high seas or before the goods reach the port of destination. It enables the buyer to clear the goods through customs under their name.
Re-import Bill of Entry: Used for goods that were previously exported and are being re-imported into the country. It allows for duty exemption or refund based on certain conditions.
Project Import Bill of Entry: Specifically for goods imported for projects, such as construction or infrastructure development, subject to specific customs duty rates and regulations.
Transshipment Bill of Entry: Filed when goods are transferred from one conveyance (such as a ship or aircraft) to another in the same port or airport for onward transportation to a different destination.
Postal Bill of Entry: Used for goods imported through postal services, typically for personal or small-scale commercial shipments, subject to specific customs procedures and duties.
Who Needs to Issue a Bill of Entry?
A Bill of Entry (BOE) is required to be issued by companies importing goods from other countries or enterprises selling goods purchased from Special Economic Zones within India. This document is essential for customs clearance procedures and allows importers to claim Input Tax Credit (ITC) on the imported items. Upon submission of the BOE, a customs officer conducts inspections to verify the goods, after which the importer is liable to pay applicable taxes, including GST, IGST, and customs duty.
Importers can then seek compensation for GST and IGST through ITC, but not for customs duty. The BOE serves as a crucial document in the importation process, ensuring compliance with customs regulations and facilitating the smooth movement of goods across borders.
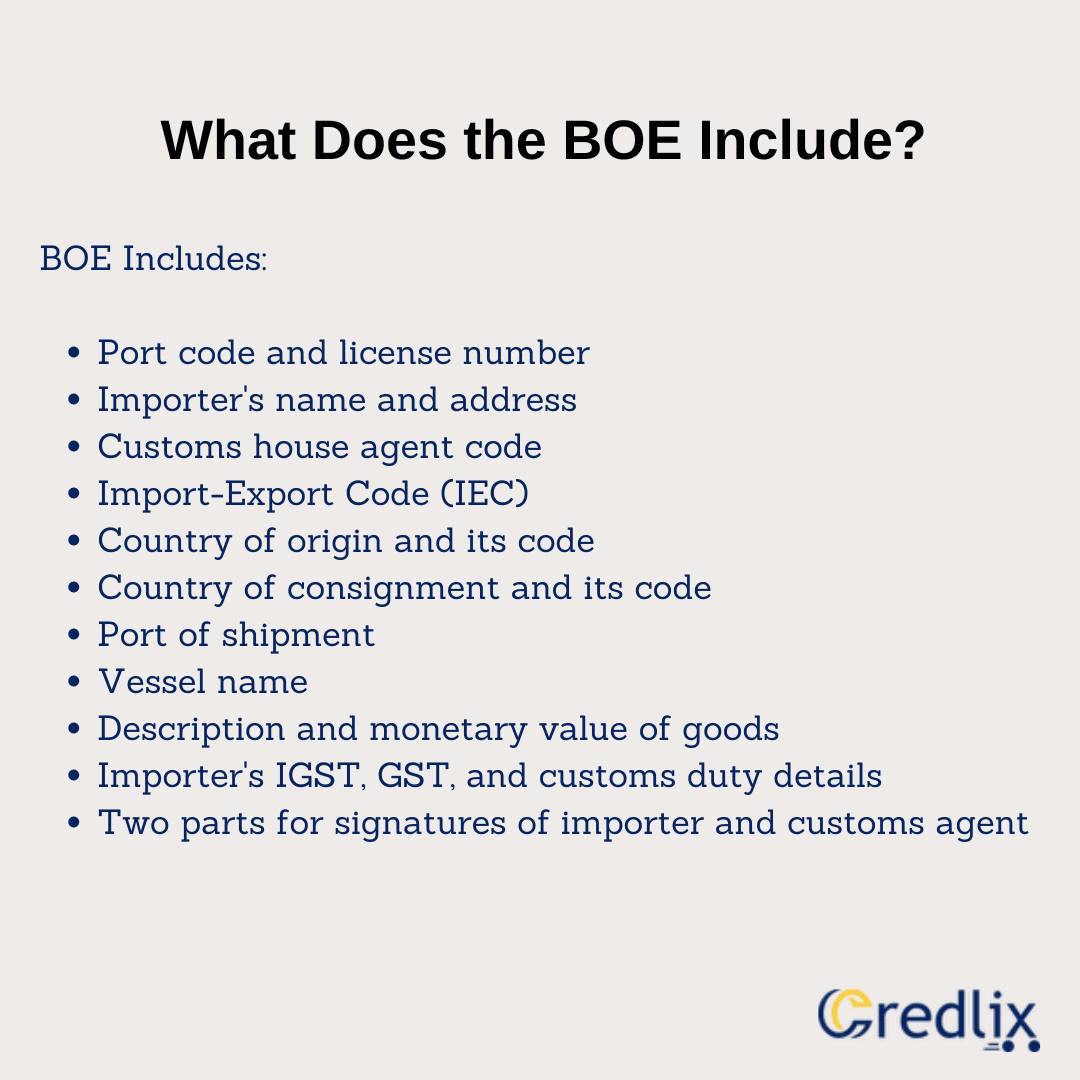
Who Prepares the Bill of Entry?
The Bill of Entry (BOE) is prepared either by the importer themselves or by a licensed customs broker. It’s a formal document filed with the customs department to facilitate the clearance of goods from customs.
How to file a Bill of Entry?
Filing a Bill of Entry (BOE) can be done through either offline or online methods, with the latter gaining prominence due to its efficiency and convenience. While manual offline filing remains an option, online forms are increasingly preferred, offering a streamlined process and minimizing interaction with customs officials.
Many customs offices now provide online portals and shipping service providers offer gateways for BOE submission, simplifying the process significantly.
Two common avenues for online filing include the Indian Customs Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) System and through a customs house agent’s server. These digital platforms facilitate smoother documentation, faster processing, and enhanced transparency in the customs clearance process, ultimately benefiting importers and exporters alike.
What is the Indian Customs Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) System?
The Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) portal serves as a digital platform accessible to both importers and customs house agents (CHAs) post-BOE filing. Users can access the portal’s website, register as certified importers, and electronically submit the BOE along with necessary documents. Particularly beneficial for novice importers entering international trade, this portal offers convenience and efficiency, especially for those yet to establish relationships with established logistics service providers.
What’s Customs House Agent’s Server
India has introduced the Indian Customs Electronic Gateway, ICEGATE, an online platform for Customs House Agents (CHAs) to fulfill their responsibilities efficiently. CHAs can register on the portal by submitting necessary details, including their license number. With their expertise in online BOE filing, CHAs offer valuable assistance to importers in navigating the process seamlessly. Even experienced importers can leverage their proficiency to ensure smooth execution of BOE-related procedures through ICEGATE.
What Documents are Required To File a BOE?
To file a BOE with customs, importers need to prepare several documents, including duplicates and photocopies, along with a draft of the BOE. Essential details such as the Goods and Services Tax Identification Number (GSTIN) must be included in the BOE for processing. Find more below:

Difference Between a BOE and a Shipping Bill
The difference between a BOE and a shipping bill is simple:
- A BOE is for importing goods into a country, filed by the importer.
- A shipping bill is for exporting goods out of a country, filed by the exporter.
- Unlike a BOE, a shipping bill doesn’t include IGST details because it deals with exporting goods.
In conclusion, India’s Bill of Entry is a crucial document in the customs clearance process, serving as the gateway for goods entering the country. It ensures compliance with customs regulations, facilitates trade activities, and maintains transparency in international transactions. With a clear understanding of the BOE, importers, exporters, and customs agents can navigate the complexities of customs procedures efficiently. Embracing digital platforms like the Indian Customs EDI System and ICEGATE further streamlines the process, enhancing convenience and transparency for all stakeholders involved.
Also Read: How to Download Shipping Bills from ICEGATE?[/vc_column_text][vc_empty_space height=””][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/3″ offset=”vc_hidden-sm vc_hidden-xs” el_class=”post-col” css=”.vc_custom_1638872146414{padding-left: 50px !important;}”][vc_widget_sidebar sidebar_id=”consulting-right-sidebar” el_id=”single-right-siebar”][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text][/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row css=”.vc_custom_1638349264629{padding-top: 100px !important;padding-bottom: 80px !important;}”][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”Related Post” font_container=”tag:h2|font_size:25px|text_align:center|color:%233c3c3c” google_fonts=”font_family:Poppins%3A300%2Cregular%2C500%2C600%2C700|font_style:600%20semi-bold%3A600%3Anormal” css=”.vc_custom_1638774169659{margin-bottom: 30px !important;}”][vc_raw_html]JTVCc21hcnRfcG9zdF9zaG93JTIwaWQlM0QlMjIxMDAwNSUyMiU1RA==[/vc_raw_html][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]