[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text][/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row el_class=”padding-sm-bottom-40″][vc_column offset=”vc_col-lg-8 vc_col-md-8″ el_class=”post-details-sec”][vc_single_image image=”11743″ img_size=”full” css=”.vc_custom_1704175916879{margin-bottom: 44px !important;}”][vc_row_inner css=”.vc_custom_1608297138483{margin-bottom: 0px !important;}”][vc_column_inner][vc_column_text]In India, goods and services that fall under the GST (Goods and Services Tax) system are sorted out using HSN (Harmonized System of Nomenclature) codes and SAC (Service Accounting Code). These codes play a crucial role in facilitating international trade by simplifying the identification of products and services. HSN codes are assigned to goods, while SAC codes are designated for services. Both codes are also incorporated into invoices and record-keeping processes.
The HSN code, or Harmonized System of Nomenclature, categorizes goods to streamline taxation. It’s like a universal language for products, making it easier for businesses to communicate across borders. On the other hand, the SAC code, or Service Accounting Code, is specifically for services. It serves a similar purpose as the HSN code but is tailored to classify various services under the GST framework.
Having these codes on invoices and records simplifies the entire taxation process, helping businesses and authorities quickly identify the nature of products or services being provided. This not only ensures a smoother domestic taxation system but also promotes efficiency in international trade by removing obstacles related to product and service categorization.
What is an HSN Code?
An HSN code, short for Harmonized System of Nomenclature code, is a globally recognized product classification system proposed by the World Customs Organization (WCO). The purpose of this code is to provide a uniform classification for goods on an international scale. India adopted the use of HSN codes in 1986, employing them to categorize goods and items for Customs and Central Excise tariff duty.
The same HSN tariff numbers used in Customs are also applied to GST (Goods and Services Tax) invoices. Essentially, HSN codes serve as a standardized method for classifying products, ensuring consistency and facilitating seamless communication in international trade.
What is the HSN code in GST?
In GST (Goods and Services Tax), the HSN code is a classification system with a six-digit base. To enhance clarity, Customs and Central Excise authorities introduced an additional two digits, resulting in a total of eight digits for the defined HSN code. The first two digits of the HSN code represent the GST chapter number, while the subsequent two digits signify chapter headings. The next two digits indicate a subheading, and the final two digits represent a further subheading, providing a detailed classification of goods.
The HSN code system encompasses 21 sections, 99 chapters, 1244 headings, and 5224 subheadings, offering a comprehensive framework for categorizing various products and facilitating streamlined taxation processes.
Applicability Requirements For HSN Code
The HSN code requirements in India vary based on annual revenue, with a three-tiered structure ranging from no code for smaller businesses to an eight-digit code for those managing import and export activities.

What is a SAC Code?
“SAC” refers to Service Accounting Code, a categorization system created by the service tax department in India for services. The GST Council has adopted SAC codes to apply the Goods and Services Tax (GST) in the country. These codes streamline the classification of services, facilitating the accurate imposition of GST.
What is the SAC Code in GST?
The Service Accounting Code (SAC) in GST is a 6-digit code defined by GST law. For instance, the SAC for IT design and development services is 998314. All services share the commonality of the first two digits, denoted by ’99.’
In this example, the middle two digits (’83’) pinpoint IT services as the major type, while the final two digits (’14’) specify the details specific to Design and Development services. The SAC system thus efficiently categorizes and delineates various services for precise taxation under GST.
Navigating GSTR Filing Requirements Based on Turnover
Explore SAC code compliance in GSTR filing:
SAC Code in GSTR Filing: Service providers must use SAC codes when completing GSTR forms.
Service Categories: Applicable to a range of services including hospitality, education, finance, and more.
Chapter 99 in HSN Module: All services fall under Chapter 99 of the HSN module dedicated to services.
Mandatory Inclusion in GSTR Forms: GSTR forms require the inclusion of the SAC code for accurate service categorization.
Turnover Below Rs. 1.5 Crores: Not mandatory for companies with a turnover less than Rs. 1.5 crores.
Turnover Between Rs. 1.5 to 5 Crores: Mandatory for companies with turnovers ranging from Rs. 1.5 to 5 crores.
Turnover Exceeding Rs. 5 Crores: Specifying SAC codes is a requirement for companies with turnovers exceeding Rs. 5 crores.
Difference Between HSN and SAC Code in GST: A Comprehensive Overview
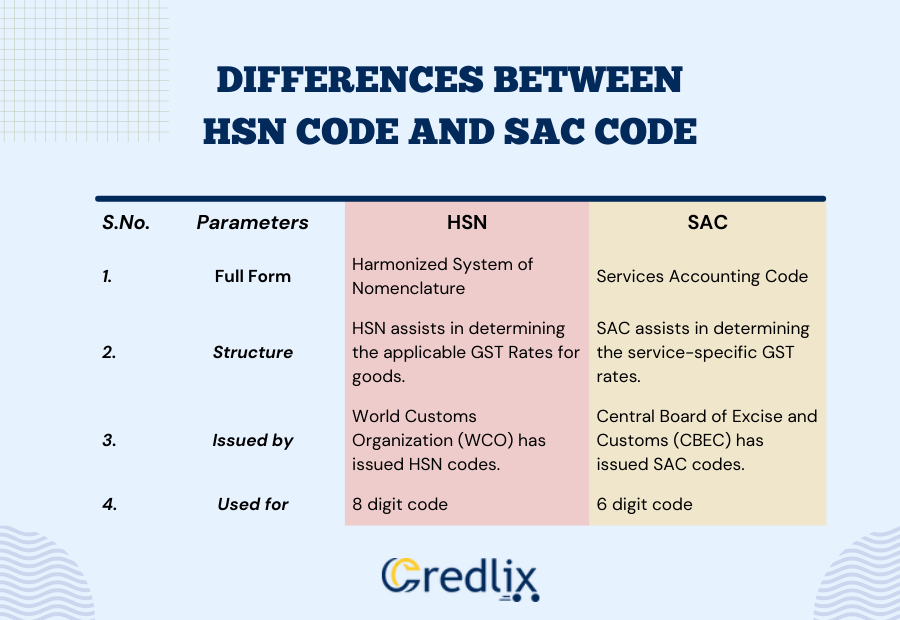
The Harmonized System of Nomenclature (HSN) code and Service Accounting Code (SAC) are crucial components of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) system in India. Understanding the disparities between HSN and SAC codes is essential for businesses navigating the complexities of taxation. Here’s an in-depth exploration of the distinctions:
1. Nature of Classification
- HSN Code: Primarily deals with the classification of goods based on a standardized international system. It encompasses products and tangible items, providing a universal language for their categorization in both domestic and international trade.
- SAC Code: Focuses on the classification of services. It is specific to the nature of services provided, offering a structured framework for accurate identification and taxation within the GST system.
2. Composition
- HSN Code: Comprises a total of eight digits. The first two digits denote the GST chapter number, followed by two digits indicating chapter headings, and the last four digits offering detailed classification up to the subheading level.
- SAC Code: Consists of a six-digit code, providing a more concise structure. The first two digits (’99’) are common for all services, the next two digits represent the major type of service, and the final two digits specify the details pertaining to a particular service.
3. Applicability Based on Turnover
- HSN Code: The requirement for using HSN codes varies according to the annual revenue of businesses. Smaller businesses with turnover below Rs. 1.5 crores are exempt from using HSN codes, while larger businesses with turnovers exceeding Rs. 5 crores must employ a 4-digit HSN number.
- SAC Code: Mandatory for all service providers in GSTR filing, regardless of turnover. The SAC code is a vital component for accurately categorizing and taxing services.
4. Purpose and Scope
- HSN Code: Primarily designed for the classification of tangible goods, facilitating international trade by providing a standardized system for product identification.
- SAC Code: Tailored to services, streamlining the classification and taxation of diverse service categories, including hospitality, education, finance, and more.
5. Integration with GSTR Forms
- HSN Code: Utilized in GSTR forms, particularly for businesses dealing with import and export. It plays a crucial role in accurate record-keeping and invoice generation.
- SAC Code: Mandatory in GSTR forms for service providers, ensuring precise categorization and taxation of various services under the GST framework.
While both HSN and SAC codes serve the purpose of systematic classification under GST, the key distinction lies in their focus – HSN for goods and SAC for services. Understanding their nuances is pivotal for businesses to comply with GST regulations and ensure accurate taxation in the diverse landscape of trade and services.
Where to Mention the HSN/SAC Code in GST Documentation
In the realm of Goods and Services Tax (GST), it is crucial for taxpayers to incorporate the HSN (Harmonized System of Nomenclature) code for goods or the SAC (Service Accounting Code) for services in various instances:
Registration for GST
When registering for GST, businesses must specify the category of products and services they deal with. Providing the accurate HSN or SAC code during registration is essential for compliance.
GST Rate Determination
Knowledge of the HSN or SAC code allows taxpayers to swiftly ascertain the applicable GST rate for goods and services, aiding in accurate tax calculations.
GST Invoice Generation
In the creation of invoices for both goods and services, sellers are mandated to include the respective HSN or SAC code. This coding is based on the overall turnover of the business and contributes to transparent invoicing practices.
GST Returns Submission
The HSN Summary, reflecting the categorization of products and services, must be included in the GST return submitted by the taxpayer. This ensures comprehensive reporting of sold goods and services, aligning with the designated HSN or SAC codes.
Ensuring the inclusion of HSN/SAC codes at these crucial junctures not only fosters GST compliance but also promotes transparency in business dealings, facilitating accurate tax determination and reporting.
Why are HSN and SAC Codes Important for Business?
Both HSN and SAC codes are important for the following reasons:
Accurate Tax Calculation
HSN (Harmonized System of Nomenclature) codes for goods and SAC (Service Accounting Code) for services are vital for precise tax determination. They enable businesses to calculate GST accurately based on the specific category and nature of the products or services provided.
Uniform International Trade
HSN codes, being a globally recognized product classification system, promote uniformity in international trade. This standardized coding system facilitates seamless communication and understanding of products across borders, easing the complexities of cross-border transactions.
Compliance with GST Regulations
In the context of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) framework, adherence to HSN and SAC codes is mandatory for businesses. Including these codes in registrations, invoices, and returns ensures compliance with GST regulations, preventing potential penalties or legal issues.
Efficient Record-Keeping
HSN and SAC codes play a crucial role in efficient record-keeping. They help businesses categorize and organize information systematically, facilitating streamlined documentation processes, especially during audits or financial reviews.
Transparent Invoicing
Including HSN and SAC codes in invoices enhances transparency in business transactions. It provides clarity to both sellers and buyers regarding the nature of goods or services being exchanged, contributing to a transparent and trustworthy business environment.
GST Rate Determination
Knowledge of the appropriate HSN or SAC code enables businesses to quickly determine the applicable GST rate for goods and services. This helps in accurate tax planning and budgeting, preventing miscalculations or errors in tax liabilities.
Facilitation of International Trade Agreements:
HSN and SAC codes play a crucial role in international trade agreements and negotiations. They provide a common language for classifying goods and services, facilitating smoother negotiations and collaborations between businesses and governments from different countries.
Also Read: HSN Codes: What You Need to Know for Trade and Taxation
Final Words
The utilization of HSN and SAC codes in the GST framework is indispensable for businesses. These codes ensure accurate tax calculations, promote uniformity in international trade, and enhance compliance with GST regulations. Efficient record-keeping, transparent invoicing practices, and the facilitation of international trade agreements further underscore their importance.
By incorporating these codes during registration, invoicing, and returns, businesses not only comply with regulatory requirements but also establish a foundation for transparent and streamlined operations, contributing to the overall success and integrity of the GST system and international trade practices.
FAQs
What makes HSN codes unique?
Every HSN code assigned to a product stands out as distinct. The extensive categorization involves 21 sections and 99 chapters encompassing all products and services. Within these chapters, there are 1244 headers and 5244 subheadings. The HSN code system employs specific rules to create an 8-digit code for each item, ensuring a unique identifier for every product used in trade or commercial activities.
Is the HSN Code Uniform Across Countries?
The HSN (Harmonized System of Nomenclature) is developed by the World Customs Organization (WCO) to categorize products. All nations under the WCO share similar HS codes, utilizing a common six-digit HSN number for their products. However, some countries opt for an 8-digit code to further sub-classify specific products or groups within their trade systems.
Is it necessary to include the HSN code in the invoice?
The inclusion of the HSN code in an invoice is mandatory for dealers or taxpayers only if their annual revenue exceeds 1.5 Crores.
Is the HSN Code Uniform Across Countries?
The development of the HSN (Harmonized System of Nomenclature) falls under the purview of the World Customs Organization (WCO), serving as a global framework for product categorization. Nations affiliated with the WCO share comparable HS codes, employing a standard six-digit HSN number for their products. However, certain countries may opt for an 8-digit code to further sub-classify specific products or groups within their trade systems.
Also Read:< Demystifying HSN Codes: Impact on Your Business and Its Significance[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text]In the dynamic world of business, managing finances efficiently is key to ensuring sustained growth and success. One crucial aspect that often takes center stage is the management of receivables – the money owed to your business by customers.
This blog aims to shed light on the strategic use of financing receivables and the impactful practice of vendor financing, offering insights that are both accessible and beneficial to businesses of all sizes.
Financing Receivables:- What is Financing Receivables

Accounts receivable financing is a different way to get money compared to going to a regular bank. Basically, it’s a money move where you borrow cash using the money your customers owe you.
Here’s the deal: if your company is waiting for money to come in, but you need cash ASAP to cover your bills, accounts receivable financing steps in to help. It’s also great for businesses that don’t want to hassle with collecting money from people who owe them. Instead, they can pay a little fee and get the money right away.
In simple terms, it’s like turning the future money you’re expecting into real cash when you need it!
Types of Financing Receivables
Here are different types of financing receivables options that you need to understand:
Collateralized Loan Option
- If you have customers who owe you money, you can use these accounts as collateral for a loan from a financing company.
- When your customers settle their bills, you can use that money to pay off the loan.
Invoice Factoring Option
- Another way is to sell your accounts receivable to a factoring company.
- With a service known as invoice factoring, the factoring company buys your non-delinquent unpaid invoices.
- They pay you an upfront percentage, called the advance rate, of what your customers owe.
- The factoring company then collects payments directly from your customers, and once the accounts receivable are paid, they keep a small factoring fee and give you the remaining balance.
Advantages of Financing Receivables
Understand some of the benefits of financing receivables to help you make a wiser and informed decision:
Upfront Cash for Unpaid Accounts: With receivables financing, you receive immediate funds for invoices that your customers haven’t paid yet. It’s like getting a cash advance based on the money you’re expecting to receive in the future.
Potentially Lower Financing Costs: The financing rate in receivables financing may be more cost-effective compared to other borrowing options such as traditional loans or lines of credit. This can be particularly beneficial for businesses looking to manage their costs while accessing the necessary funds.
Relief from Unpaid Bill Collection: Opting for receivables financing can lift the weight of chasing down unpaid bills from your shoulders. Instead of spending time and resources on collections, a financing company takes on this task. It allows your business to focus on its core activities while ensuring a steady flow of working capital.
Ideal for Cash Flow Challenges: Receivables financing is a great solution for businesses facing cash flow issues. Whether you’re waiting for payments from customers or need quick funds to cover operational expenses, this option provides a flexible and accessible way to address cash flow gaps. It’s suitable for a variety of companies, regardless of their size or industry, offering a lifeline during financially challenging periods.
Disadvantages of Financing Receivables
Understand some of the cons of financing receivables to help you make a wiser and informed decision:
Requirement of Outstanding Invoices: To benefit from receivable financing, your business must have outstanding invoices, meaning customers owe you money. This financial option leverages these accounts receivable as assets that can be used to secure a loan or sell to a factoring company.
Importance of Clear Terms for Unpaid Accounts: Keeping clear and accurate records of the terms associated with unpaid accounts is crucial. This includes documenting when payments are expected, the amounts owed, and any specific conditions. Maintaining meticulous records is essential for the smooth process of receivable financing, ensuring transparency and accuracy in the transactions.
Impact of Credit History on Qualification: Qualifying for receivable financing may depend on your business’s credit history. If your business lacks a stable credit history, it could pose a challenge in accessing this form of financing. Lenders or factoring companies often assess the creditworthiness of a business before extending receivable financing. Having a stable credit history enhances your eligibility and may lead to more favorable terms. It emphasizes the importance of maintaining good financial standing to maximize the benefits of receivable financing.
Vendor Financing:- What is Vendor Financing?

Vendor financing, also known as supplier financing or trade credit, is a financial arrangement where a company obtains funding or extended payment terms from its suppliers. In this scenario, the vendor, or the supplier of goods or services, plays a crucial role in providing financial support to the purchasing company.
It’s a smart move when you’re buying a lot of big stuff. If you’re getting things like inventory for a store, computers, vehicles, or machinery, talk to your suppliers about financing deals. It’s like making a deal to pay for these things over time instead of all at once. This helps you avoid running low on cash and gives you the chance to grow your business while paying for the equipment. It’s a win-win!
Also Read : What Is a Vendor? Definition, Types, and Example
Benefits of Vendor Financing
Understand some of the benefits of vendor financing to help you make a wiser and informed decision:
Equipment Purchase without Upfront Payment: One big advantage of vendor financing is that it lets you buy the equipment you need without having to pay for it all upfront. Instead of emptying your wallet in one go, you can work out a deal with your vendor to spread the cost over time. This means you can get essential equipment for your business without a hefty immediate expense.
Preservation of Cash for Emergencies: By using vendor financing, you’re able to keep more cash on hand. This is crucial for dealing with unexpected emergencies or opportunities that may come up in your business journey. Preserving your cash flow provides a financial safety net, allowing you to handle unforeseen challenges without disrupting your day-to-day operations or long-term plans.
Also Read: How to Use Vendor Financing to Buy a Business?
Disadvantages of Vendor Financing
Understand some of the cons of financing receivables to help you make a wiser and informed decision:
Extended Payment Period: One downside of vendor financing is that your payments might stretch out over a long period. While this eases the immediate financial burden, it could mean you’re committed to paying for the equipment over an extended timeframe. This extended payment period may limit your financial flexibility and tie up resources that could be used for other business needs.
Risk of Equipment Retrieval: If you fall behind on your payments, there’s a risk that the vendor could take back the equipment. This is a significant concern because it means not keeping up with your agreed-upon payment schedule could result in losing the very equipment your business relies on. It emphasizes the importance of carefully managing your financial commitments to avoid potential disruptions to your operations.
Distinguishing Accounts Receivables Finance from Accounts Receivable Factoring
Navigating the world of turning accounts receivables into immediate cash flow can be a game-changer for businesses in need of quick funds. While both services share the common goal of providing timely financial solutions, it’s essential to understand their fundamental differences:
Nature of the Transactions
Accounts Receivables Finance (Invoice Financing)
Think of this as a loan. Your business uses its outstanding invoices as collateral to secure a loan. It’s a financial arrangement where you borrow against the money your customers owe you, providing a flexible solution to bridge financial gaps.
Accounts Receivable Factoring
In contrast, factoring involves the outright sale of your receivables. Factoring companies become the owners of the current asset – your unpaid invoices. They pay you a portion upfront (known as the advance), and then they collect the full amount directly from your customers.
Roles of the Service Providers
Factoring Companies
Factoring companies act as buyers of a business’s current assets, taking ownership of the accounts receivable. They assume the responsibility of collecting payments from your customers.
Accounts Receivable Financing Companies
On the other hand, companies providing accounts receivable financing act as financiers or lenders. They extend a loan to your business, using the outstanding invoices as collateral, without taking ownership of the receivables.
Scope of Application
Accounts Receivable Factoring
Factoring is specifically tailored for commercial financing. It is a solution designed for businesses looking to optimize their cash flow by selling their unpaid invoices in commercial transactions.
Final Words
In the world of business, managing finances wisely is the key to success. Whether it’s unlocking cash through accounts receivables financing or securing equipment with vendor financing, these financial tools offer both opportunities and considerations. Accounts receivables financing turns future money into immediate cash, ideal for addressing cash flow challenges.
Vendor financing, on the other hand, lets you spread the cost of essential equipment, preserving cash for emergencies. While each has its advantages, it’s crucial to weigh the pros and cons. Whether you’re considering accounts receivables financing or vendor financing, understanding these financial strategies empowers you to make informed decisions, propelling your business toward sustained growth and financial resilience.
Credlix is becoming a big player in helping businesses with money. We want to make small businesses stronger, so we offer really good financing solutions made just for them.
Also Read : What Is a Vendor? Definition, Types, and Example[/vc_column_text][vc_empty_space height=””][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/3″ offset=”vc_hidden-sm vc_hidden-xs” el_class=”post-col” css=”.vc_custom_1638872146414{padding-left: 50px !important;}”][vc_widget_sidebar sidebar_id=”consulting-right-sidebar” el_id=”single-right-siebar”][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text][/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row css=”.vc_custom_1638349264629{padding-top: 100px !important;padding-bottom: 80px !important;}”][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”Related Post” font_container=”tag:h2|font_size:25px|text_align:center|color:%233c3c3c” google_fonts=”font_family:Poppins%3A300%2Cregular%2C500%2C600%2C700|font_style:600%20semi-bold%3A600%3Anormal” css=”.vc_custom_1638774169659{margin-bottom: 30px !important;}”][vc_raw_html]JTVCc21hcnRfcG9zdF9zaG93JTIwaWQlM0QlMjIxMDAwNSUyMiU1RA==[/vc_raw_html][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]