[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text][/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row el_class=”padding-sm-bottom-40″][vc_column offset=”vc_col-lg-8 vc_col-md-8″ el_class=”post-details-sec”][vc_single_image image=”12275″ img_size=”full” css=”.vc_custom_1709703670172{margin-bottom: 44px !important;}”][vc_row_inner css=”.vc_custom_1608297138483{margin-bottom: 0px !important;}”][vc_column_inner][vc_column_text]India is rapidly becoming a key player in global trade, with its export sector booming. The Ministry of Commerce and Industry reports that India’s export trade for April-February 2020-21 reached an impressive $439 billion. To facilitate this growth and ensure smooth transactions between Indian exporters and foreign buyers, the Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT) was established.
Headquartered in New Delhi, DGFT operates as an agency under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry of the Government of India. Its primary objective is to design and execute the Foreign Trade Policy of the country. This policy framework is crucial as it sets the guidelines and rules for India’s international trade dealings. DGFT plays a pivotal role in nurturing and enhancing trade relationships with various countries, thereby facilitating seamless exports. Additionally, it is responsible for issuing export licenses and introducing trade incentives to promote exports further.
DGFT operates through a network of zonal and regional offices across India. It has four zonal offices located in New Delhi, Mumbai, Kolkata, and Chennai, each headed by a Zonal Joint Director General of Foreign Trade. These offices serve as key points of contact for exporters, providing guidance and support throughout the export process. Furthermore, DGFT has 35 Regional Authorities spread across the country, ensuring accessibility to its services for businesses nationwide.
Understanding the functions of DGFT is essential for both existing and aspiring exporters in India.
Functions of DGFT
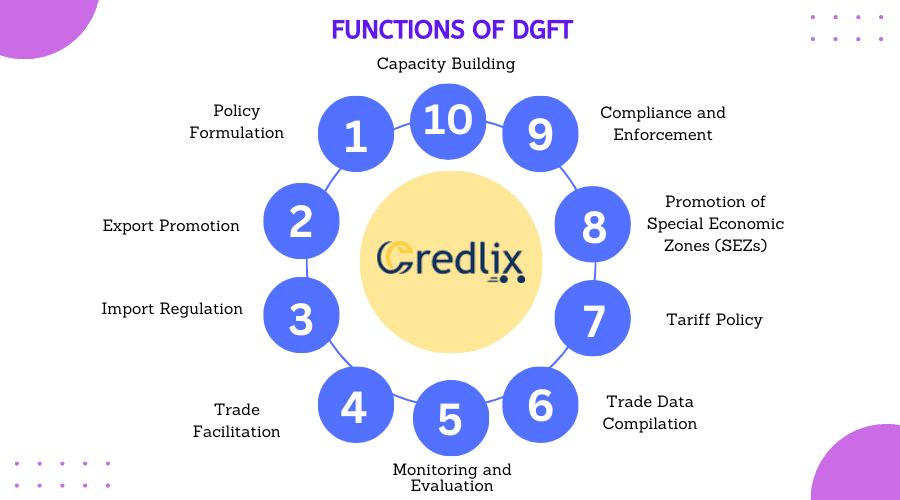
The Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT) plays a crucial role in facilitating and regulating India’s international trade. Here are ten key functions of the DGFT, elaborated:
Policy Formulation: DGFT formulates foreign trade policies and measures to promote and regulate India’s international trade, taking into account economic, social, and commercial interests.
Export Promotion: It designs and implements various schemes and programs to promote Indian exports, such as the Export Promotion Capital Goods (EPCG) Scheme and the Merchandise Exports from India Scheme (MEIS).
Import Regulation: DGFT regulates and controls the import of certain goods through mechanisms such as licensing, quotas, and restrictions to ensure the balance of trade and safeguard domestic industries.
Trade Facilitation: It facilitates trade by simplifying procedures, reducing paperwork, and providing online platforms for quick and efficient processing of various trade-related transactions and documents.
Monitoring and Evaluation: DGFT monitors and evaluates the effectiveness of trade policies and schemes, analyzing their impact on export performance, foreign exchange earnings, and overall economic development.
Trade Data Compilation: It collects, compiles, and analyzes trade data to assess trends, identify potential markets, and formulate strategies for enhancing India’s competitiveness in global trade.
Tariff Policy: DGFT formulates tariff policies and trade agreements to negotiate favorable terms for Indian exporters and ensure fair competition in international markets.
Promotion of Special Economic Zones (SEZs): DGFT plays a key role in promoting SEZs by granting approvals, providing incentives, and facilitating trade within these designated zones to attract foreign investment and boost exports.
Compliance and Enforcement: It ensures compliance with trade regulations and policies through monitoring, inspections, and enforcement actions against violations such as smuggling, illegal trade practices, and non-compliance with export-import norms.
Capacity Building: DGFT conducts training programs, workshops, and seminars to build the capacity of exporters, importers, and other stakeholders, equipping them with the knowledge and skills necessary to effectively engage in international trade.
Overall, the DGFT serves as a central authority responsible for formulating, implementing, and monitoring policies and measures aimed at promoting India’s foreign trade while safeguarding its economic interests.
Services Offered By Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT)
The Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT) offers a range of services aimed at promoting exports and assisting Indian businesses in navigating the complexities of international trade. Here’s an elaboration on some of the key services provided:
DGFT Helpdesk Service: DGFT operates a comprehensive helpdesk service to address inquiries, provide guidance, and offer assistance to exporters on various aspects of foreign trade regulations, procedures, and policies. This service acts as a valuable resource for exporters seeking clarification or guidance on export-related matters.
IEC and Profile Management: DGFT facilitates the issuance and management of Importer Exporter Code (IEC) numbers, which are essential for businesses engaged in importing or exporting goods and services. Through its platform, DGFT enables exporters to apply for and manage their IEC profiles efficiently, streamlining the process of obtaining necessary licenses and permissions.
Duty Free Import Authorization (DFIA): The Duty Free Import Authorization (DFIA) scheme is designed to promote exports by allowing duty-free import of inputs required for the production of export goods. DGFT administers this scheme, granting authorizations to eligible exporters, thereby reducing the cost of production and enhancing the competitiveness of Indian goods in international markets.
Online E-com Application: DGFT offers an online platform for exporters to submit applications and documents electronically, streamlining the process of obtaining various licenses, authorizations, and incentives. This e-commerce application system enhances efficiency, transparency, and accessibility, enabling exporters to conduct business transactions conveniently from anywhere.
Export Promotion Capital Goods (EPCG) Scheme: Under the Export Promotion Capital Goods (EPCG) scheme, DGFT provides incentives to exporters for importing capital goods at concessional or zero duty rates, subject to fulfillment of export obligations. This scheme aims to encourage investment in technology upgradation and modernization of export-oriented industries, thereby boosting exports and enhancing India’s competitiveness.
Merchandise or Service Exports Scheme and Policy: DGFT formulates and implements policies and schemes to promote both merchandise and service exports. These policies encompass various incentives, concessions, and support mechanisms tailored to incentivize and facilitate export activities across different sectors, contributing to the overall growth of India’s export trade.
Import-Export Management System: DGFT operates an Import-Export Management System (IEMS) to facilitate the electronic processing of export-import transactions, including online filing of documents, tracking of shipments, and monitoring compliance with trade regulations. This integrated platform enhances the efficiency, transparency, and accountability of trade operations, enabling exporters to navigate the import-export process seamlessly.
In essence, DGFT plays a pivotal role in providing comprehensive support services and facilitating a conducive environment for exporters, thereby fostering the growth of India’s export sector and contributing to the nation’s economic development.
The Role of DGFT Digital Signature Certificate
The DGFT Digital Signature Certificate (DSC) is a crucial component introduced by the Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT) to ensure the authenticity and security of exporters and their associated documents in the realm of online transactions. This digital certificate has been mandated by the DGFT for use with all electronic documents uploaded on its website, thereby enhancing the integrity and reliability of digital transactions within the export-import ecosystem.
By requiring the use of DSC, DGFT aims to instill a high level of trust and security in online interactions by guaranteeing the privacy and confidentiality of exchanged information. The DSC serves as a digital seal of authenticity, providing assurance that the documents and transactions are legitimate and have not been tampered with.
One of the primary functions of the DGFT DSC is to strengthen and streamline the process of Importer Exporter Code (IEC) issuance and modification. This ensures that only authorized entities with valid credentials can access and modify crucial trade-related documents, thereby minimizing the risk of fraudulent activities and unauthorized access.
The utilization of DSC facilitates exporters and importers in seamlessly filing and applying for various documents on the DGFT website, ensuring complete authenticity and compliance with regulatory requirements. Furthermore, obtaining a DSC is an essential step in the licensing process, as it serves as a key verification mechanism for the identity and credibility of the business entity.
It is imperative to note that the DGFT mandates the use of Class-2 or Class-3 DSCs, which are issued only by agencies certified by the Controller of Certifying Authorities (CCA) in India. This stringent requirement ensures that the digital certificates meet the highest standards of security and authenticity, providing exporters with peace of mind regarding the integrity of their online transactions.
7 Ways How DGFT Regulates Export from India?
Discover DGFT’s diverse methods for regulating Indian exports, ensuring compliance, facilitating transactions, and analyzing trade data effectively.
Foreign Trade Procedures
DGFT plays a pivotal role in devising and disseminating foreign trade procedures, crucial for exporters in India. These procedures are meticulously crafted to ensure simplicity and user-friendliness, thereby facilitating smooth execution of foreign trade activities within the country.
By providing clear guidelines and regulations, DGFT empowers exporters to navigate the complexities of international trade with ease, promoting efficiency and compliance while fostering a conducive environment for trade growth and expansion.
Streamlined Process for Exporters and Importers
Applying for an Importer-Exporter Code (IEC) is now hassle-free for aspiring exporters. Sellers can obtain this 10-digit unique registration code directly from the DGFT website, right from the comfort of their homes, at any time. The IEC simplifies tracking and managing shipments for both exporters and importers, ensuring smooth trade operations.
The EXIM Policy/Foreign Trade Policy
For smooth export-import operations, countries require clear guidelines. The EXIM policy, also known as the Foreign Trade Policy, fulfills this need by providing essential instructions to oversee export businesses. Developed by the DGFT, these guidelines are periodically announced by the Government of India under Section 5 of the Foreign Trade Act 1992.
Lasting for a period of five years, the policy framework serves as a roadmap, outlining strategies and regulations to facilitate trade relations. It aims to promote exports, boost economic growth, and ensure compliance with international trade standards. By offering a structured approach to trade, the EXIM policy contributes to maintaining healthy trade relations while fostering a conducive environment for exporters and importers to thrive.
Also Read: EXIM Documentation: Vocabulary and Significance
ITC (Indian Trade Clarification) HS Codes
In order to foster the expansion of foreign trade, India has embraced the International Harmonized System of Coding (ITC HS codes). These codes serve as a standardized classification system, enabling exporters to accurately categorize their products and ensure correct commodity descriptions. In India, the ITC HS Codes are segmented into two schedules: Schedule 1 pertains to imports, while Schedule 2 is designated for exports.
The DGFT holds the authority to amend commodity descriptions and introduce new codes within the country, ensuring alignment with international trade standards. By adhering to these codes, exporters can streamline their trade operations, enhance transparency, and mitigate risks associated with incorrect product categorization. Ultimately, the utilization of ITC HS codes facilitates smoother trade processes, promoting growth and efficiency in India’s foreign trade sector.
DGFT’s Role in Facilitating Trade With Export Licensing
DGFT issues licenses for various products eligible for export from India, spanning popular categories like textiles, home accessories, handicrafts, and leather goods. However, for items classified as ‘restricted’ by the Government of India, such as horses and certain petroleum oils, exporters must obtain an export license from DGFT. These licenses can be conveniently applied for online through the DGFT website.
By regulating the export of restricted items, DGFT ensures compliance with government regulations while facilitating smoother trade operations. Through this process, exporters can obtain the necessary authorization to engage in the export of a wide range of products, contributing to the growth and sustainability of India’s export sector. Overall, DGFT’s issuance of export licenses plays a crucial role in promoting trade and ensuring adherence to regulatory frameworks.
DGFT Efforts in Export Promotion
DGFT plays a crucial role in promoting exports through various schemes introduced under the Foreign Trade Policy. These schemes, including the Advance Authorization Scheme, Duty Free Import Authorization Scheme, and Deemed Exports, are tailored to support sellers in their export endeavors. By availing these schemes, exporters can benefit from incentives and facilitative measures provided by the government, thereby enhancing their competitiveness in international markets.
Moreover, DGFT is committed to enhancing the ease of doing business for exporters by simplifying and digitizing export-import procedures. This initiative aims to streamline trade processes, reduce bureaucratic hurdles, and foster a more conducive environment for foreign trade. Through the implementation of user-friendly digital platforms and streamlined procedures, DGFT endeavors to promote efficiency and transparency in export-import operations.
Additionally, DGFT regularly issues notifications, public notices, and circulars to disseminate important information and updates regarding trade regulations and policies. These communications serve to keep exporters informed and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements, further facilitating smooth trade operations.
Quality Complaints & Trade Issues
DGFT serves as a platform for resolving concerns raised by exporters, diligently addressing feedback, suggestions, and trade-related issues. It handles complaints from both foreign buyers regarding Indian exporters and complaints from Indian importers against foreign suppliers. By providing a mechanism for redressal, DGFT aims to ensure fair and smooth trade operations.
Through this process, DGFT actively engages in resolving disputes and addressing grievances to maintain the integrity and reputation of India’s export trade. By fostering transparent communication and effective resolution mechanisms, DGFT endeavors to uphold the standards of quality and reliability in international trade transactions. Overall, its commitment to addressing quality complaints and trade issues underscores its dedication to facilitating a conducive environment for exporters and importers alike.
Final Note
The Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT) plays a crucial role in facilitating India’s export-import operations, ensuring smooth transactions, and promoting growth in the global market. By implementing user-friendly procedures, issuing licenses, and resolving trade issues, DGFT strives to empower exporters and importers, fostering a conducive environment for trade. With its commitment to simplifying processes and promoting transparency, DGFT continues to be a cornerstone of India’s trade ecosystem, contributing to the country’s economic development and international competitiveness.
Also Read: How Exim policies have evolved in the last 75 years in India[/vc_column_text][vc_empty_space height=””][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/3″ offset=”vc_hidden-sm vc_hidden-xs” el_class=”post-col” css=”.vc_custom_1638872146414{padding-left: 50px !important;}”][vc_widget_sidebar sidebar_id=”consulting-right-sidebar” el_id=”single-right-siebar”][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text][/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row css=”.vc_custom_1638349264629{padding-top: 100px !important;padding-bottom: 80px !important;}”][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”Related Post” font_container=”tag:h2|font_size:25px|text_align:center|color:%233c3c3c” google_fonts=”font_family:Poppins%3A300%2Cregular%2C500%2C600%2C700|font_style:600%20semi-bold%3A600%3Anormal” css=”.vc_custom_1638774169659{margin-bottom: 30px !important;}”][vc_raw_html]JTVCc21hcnRfcG9zdF9zaG93JTIwaWQlM0QlMjIxMDAwNSUyMiU1RA==[/vc_raw_html][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]