[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text][/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row el_class=”padding-sm-bottom-40″][vc_column offset=”vc_col-lg-8 vc_col-md-8″ el_class=”post-details-sec”][vc_single_image image=”12773″ img_size=”full” css=”.vc_custom_1714543805931{margin-bottom: 44px !important;}”][vc_row_inner css=”.vc_custom_1608297138483{margin-bottom: 0px !important;}”][vc_column_inner][vc_column_text]The HSN, which stands for Harmonised System of Nomenclature, was introduced in 1988 by the World Customs Organization (WCO) to classify goods systematically on both national and international scales. In the context of GST, the HSN code typically consists of a 6-digit classification for various products. It’s a requirement for both business-to-business (B2B) and business-to-consumer (B2C) tax invoices for the supply of goods and services.
In India, the Ministry of Finance has made it mandatory for businesses with a turnover of Rs 5 crore and above to use the HSN code in GST. This requirement came into effect on April 1, 2021, for the supply of taxable goods and services, ensuring uniformity and transparency in taxation procedures.
Understanding HSN in GST
The Harmonized System of Nomenclature (HSN) code used in the Goods and Services Tax (GST) consists of 21 sections, further divided into 99 chapters and approximately 1244 headings. This classification system simplifies GST procedures and facilitates global acceptance. Originally, 6-digit HSN codes were utilized for classifying commodities for Customs and Central Excise, and these same codes are now employed for GST purposes.
HSN codes play a vital role in efficiently gathering and analyzing data to comprehend both foreign and domestic trades. This data aids governmental decision-making processes concerning policies related to the trade of various commodities.
Also Read: HSN Codes: What You Need to Know for Trade and Taxation
Why is HSN Code Needed?
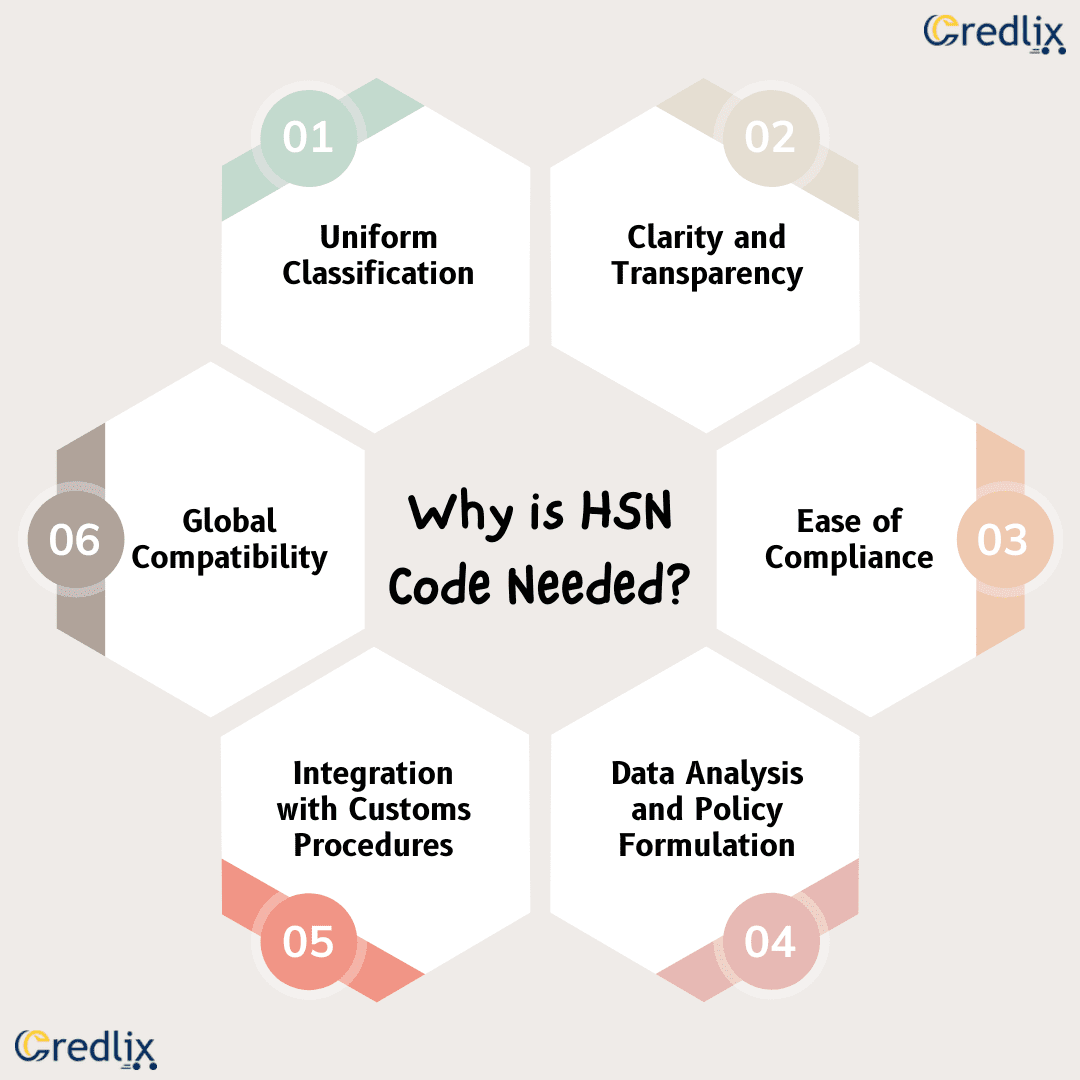
The HSN (Harmonized System of Nomenclature) code serves several critical purposes within the framework of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) regime:
Uniform Classification: It provides a uniform and systematic classification of goods across the globe, facilitating smoother international trade.
Clarity and Transparency: By assigning a specific HSN code to each commodity, it brings clarity and transparency to the tax system, reducing ambiguity and potential disputes.
Ease of Compliance: Businesses can easily determine the applicable tax rates and compliance requirements for their products by referencing the corresponding HSN code.
Data Analysis and Policy Formulation: The use of HSN codes enables efficient data collection and analysis, which helps governments in formulating effective trade policies and tax regulations.
Integration with Customs Procedures: Since HSN codes were originally used for customs and excise purposes, their integration into the GST system streamlines administrative procedures and enhances efficiency.
Global Compatibility: Being a globally accepted classification system, HSN codes facilitate international trade by ensuring compatibility with the classification systems of other countries.
The adoption of HSN codes in the GST regime fulfills the need for a standardized and structured approach to tax classification, contributing to the simplicity, transparency, and effectiveness of the tax system.
HSN Codes For Accurate Tax Classification
In India, the Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC) uses the HSN classification system to determine GST rates for goods. Therefore, businesses must accurately identify the relevant HSN Code to ascertain the applicable GST rate for their products. As of April 1, 2021, CBIC has mandated the use of specific HSN codes for GST reporting:
- For businesses with an aggregate turnover of up to 5 crore rupees in the preceding year, a 4-digit HSN Code must be mentioned.
- For businesses with an aggregate turnover exceeding 5 crore rupees in the preceding year, a 6-digit HSN Code is required.
Given the importance of correct HSN code reporting in GST, online calculators are available to assist in HSN code searches, ensuring accuracy in classification. Essentially, there are four types of HSN codes:
-
- 2-digit HSN Code:
These initial 2 digits denote the Chapter, providing a broad categorization of goods.
-
- 4-digit HSN Code:
At this level, the code represents the Heading, offering a more specific classification within a chapter.
-
- 6-digit HSN Code:
Subheadings are identified at this level, providing further granularity in classification.
-
- 8-digit HSN Code:
Tariff items are specified at this level, offering the most detailed classification.
By employing these hierarchical HSN codes, businesses can accurately classify their products for GST purposes, ensuring compliance with tax regulations and facilitating smooth trade operations.
HSN Codes in India
Introduced in India in 1986, Harmonized System of Nomenclature (HSN) codes serve the dual purpose of classifying commodities for both Customs and Central Excise. These codes, initially utilized for Customs, seamlessly transitioned into the Goods and Services Tax (GST) regime. The integration of HSN codes across Customs and GST simplified administrative processes, as the same codes apply uniformly. Moreover, HSN codes have gained global recognition, being adopted worldwide for their efficacy in categorizing various commodities.
Each commodity is assigned a specific HSN code, eliminating the necessity to provide detailed descriptions of goods during GST return filing. This streamlined approach not only saves time but also enhances efficiency in the GST filing process. Consequently, businesses benefit from reduced administrative burdens and smoother compliance procedures.
The incorporation of HSN codes in the Indian tax system represents a significant advancement, aligning the country’s trade practices with international standards and facilitating seamless cross-border transactions.
HSN Codes in GST For Simple Taxes and Trade
In the world of Goods and Services Tax (GST), the HSN code serves as a handy tool, comprising six alphanumeric characters to categorize an array of over 5000 products. Think of it as the organizational backbone, neatly arranging these diverse items into a structured system that’s both legally sound and easy to follow.
HSN codes are valuable because they rely on clear rules, ensuring consistent classification globally. They act as a universal language for trade, simplifying transactions across borders.
When it comes to taxes, HSN codes serve as helpful guides, determining the correct tax rates for each product. This enables businesses to easily calculate their tax liabilities, reducing confusion and errors.
Moreover, HSN codes facilitate the tracking of imports and domestic trade. They provide a straightforward method for monitoring the quantity of goods entering and leaving a country, enabling authorities to enforce regulations and safeguard the economy.
Classifying Goods Under HSN
Since 1986, India has been using the Harmonized System of Nomenclature (HSN) to classify goods for Central Excise and Customs purposes. This system has evolved over time, adding two extra digits to the original 6-digit structure. This update helps meet modern needs by allowing for a more detailed classification of products.
According to the latest regulations governing HSN codes, the classification structure is delineated as follows:
Chapter Number: The initial two digits of the HSN code signify the chapter number, providing a broad categorization of products based on overarching themes or characteristics.
Heading Number: Following the chapter number, the subsequent two digits represent the heading number. This intermediate level of classification offers a more detailed delineation within each chapter, narrowing down the scope to specific categories or groups of products.
Product Code: The final two digits of the HSN code correspond to the product code. This granular level of classification enables the identification of individual products or items within a specific heading, ensuring precise categorization.
Following this structured system, businesses can correctly categorize their goods under the HSN code. This makes it easier to handle taxes, customs, and trade paperwork smoothly. Using this organized method not only makes it clearer which category a product belongs to but also makes things run more smoothly and ensures that rules are followed when managing goods in different industries.
Purpose for Using HSN Code in GST
HSN codes are employed worldwide across approximately 200 countries due to their numerous advantages. Firstly, they enhance the collection of international trade data by providing a standardized classification system.
Secondly, HSN codes serve as a logical foundation for setting Customs tariffs, promoting consistency and transparency in trade regulations.
Moreover, their uniformity ensures global acceptance, simplifying cross-border transactions. While HSN codes remain consistent for most goods across countries, slight variations may occur in some cases based on the specific nature of classified items.
What are SAC Codes?
SAC, or Services Accounting Code, is a classification system specifically designed for services, in contrast to goods. Developed by the Service Tax Department of India, SAC codes play a crucial role in categorizing various services for taxation purposes. Under the GST regime, services are classified into five distinct categories based on their SAC codes, each corresponding to different tax rates: 0%, 5%, 12%, 18%, and 28%.
This systematic approach ensures clarity and consistency in the taxation of services, streamlining the process for both businesses and tax authorities. By assigning SAC codes to services, the GST framework effectively manages the taxation of services, contributing to a more transparent and efficient tax system.
D/B HSN & SAC Codes
HSN (Harmonized System of Nomenclature) codes and SAC (Services Accounting Code) are both classification systems used under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) regime in India, but they serve distinct purposes.
HSN codes primarily classify goods for taxation and trade purposes, providing a standardized system for categorizing commodities based on their nature and characteristics. These codes are used to determine the applicable GST rates for goods and simplify customs procedures.
On the other hand, SAC codes are specifically designed for classifying services. Developed by the Service Tax Department of India, SAC codes categorize various services for taxation under GST. They help in identifying the appropriate GST rate applicable to different types of services, ranging from 0% to 28%.
In summary, while HSN codes classify goods, SAC codes classify services, and both are essential for ensuring accurate taxation and compliance under the GST regime.
Benefits of HSN Code in GST
HSN (Harmonized System of Nomenclature) codes within the Goods and Services Tax (GST) framework offers several benefits:
Streamlined Taxation: HSN codes simplify the tax classification process by providing a standardized system for categorizing goods. This ensures consistency in determining applicable GST rates, reducing ambiguity and simplifying tax compliance for businesses.
Efficient Data Analysis: HSN codes facilitate the collection and analysis of data related to international and domestic trade. By categorizing goods into specific codes, governments can gather valuable insights into trade patterns, helping to inform policy decisions and economic strategies.
Ease of Trade: HSN codes provide a common language for trade, making it easier for businesses to engage in cross-border transactions. The standardized classification system enhances transparency and facilitates smoother customs procedures, ultimately fostering international trade.
Time and Cost Savings: The use of HSN codes eliminates the need for businesses to provide detailed descriptions of goods during GST filing. This saves time and reduces administrative burdens, allowing companies to focus on core operations and increasing efficiency.
Global Acceptance: HSN codes are recognized and used internationally, promoting global harmonization of trade practices. This enhances the compatibility of Indian trade data with international standards, facilitating smoother interactions with trading partners worldwide.
How to find your HSN Code?
To determine the HSN code for a product, follow these steps:
- Begin by selecting the appropriate Chapter.
- Next, choose the relevant Section.
- Filter further to identify the subheading, which provides more specific details about the product.
For example, let’s consider the HSN code for Roasted Chana, which is 19.04.10.90. In this code, “19” represents the Chapter, “04” denotes the Section, “10” indicates the subheading, and “90” specifies the product code. By following this hierarchical structure, you can accurately identify the HSN code for any given product.
Understanding the Structure of HSN Sections
The HSN (Harmonized System of Nomenclature) encompasses 21 sections, offering a comprehensive framework for classifying goods. Within this system, there are 99 Chapters, approximately 1,244 headings, and around 5,224 subheadings. Each Section is subdivided into Chapters, providing a broad classification of goods. These Chapters are further divided into Headings, offering more detailed categorization, and each Heading is then broken down into Subheadings, providing even finer distinctions.
While Sections and Chapters delineate broad categories of goods, Headings and Subheadings offer detailed descriptions of specific products. This hierarchical structure facilitates precise classification and simplifies the process of identifying HSN codes for various commodities.
In conclusion, the HSN (Harmonized System of Nomenclature) code plays a crucial role in the Goods and Services Tax (GST) regime, providing a standardized and structured approach to tax classification for both goods and services. By accurately categorizing products and services, HSN and SAC codes simplify taxation procedures, enhance transparency, and foster efficiency in trade operations.
Moreover, they facilitate data analysis, inform policy decisions, and promote global harmonization of trade practices. Businesses benefit from reduced administrative burdens and smoother compliance processes, while governments gain valuable insights into trade patterns and economic trends. Overall, the adoption of HSN and SAC codes contributes to a more transparent, efficient, and globally compatible tax system, benefiting both businesses and economies.[/vc_column_text][vc_empty_space height=””][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/3″ offset=”vc_hidden-sm vc_hidden-xs” el_class=”post-col” css=”.vc_custom_1638872146414{padding-left: 50px !important;}”][vc_widget_sidebar sidebar_id=”consulting-right-sidebar” el_id=”single-right-siebar”][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text][/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row css=”.vc_custom_1638349264629{padding-top: 100px !important;padding-bottom: 80px !important;}”][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”Related Post” font_container=”tag:h2|font_size:25px|text_align:center|color:%233c3c3c” google_fonts=”font_family:Poppins%3A300%2Cregular%2C500%2C600%2C700|font_style:600%20semi-bold%3A600%3Anormal” css=”.vc_custom_1638774169659{margin-bottom: 30px !important;}”][vc_raw_html]JTVCc21hcnRfcG9zdF9zaG93JTIwaWQlM0QlMjIxMDAwNSUyMiU1RA==[/vc_raw_html][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]