[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text][/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row el_class=”padding-sm-bottom-40″][vc_column offset=”vc_col-lg-8 vc_col-md-8″ el_class=”post-details-sec”][vc_single_image image=”12360″ img_size=”full” css=”.vc_custom_1710494936989{margin-bottom: 44px !important;}”][vc_row_inner css=”.vc_custom_1608297138483{margin-bottom: 0px !important;}”][vc_column_inner][vc_column_text]Exporters require financing to navigate the complexities of international trade successfully. Operating on a global scale demands substantial financial resources to cover expenses such as production, shipping, and compliance with trade regulations. Without adequate financing, exporters may struggle to fulfill orders, expand into new markets, or compete effectively against rivals. Additionally, the extended payment cycles common in cross-border transactions can strain cash flow, necessitating financial support to maintain business operations smoothly.
Export financing serves as a vital tool to bridge these gaps, offering businesses the liquidity and flexibility needed to capitalize on opportunities and mitigate risks inherent in the global marketplace. In essence, financing empowers exporters to navigate the challenges of international trade while unlocking the potential for sustainable growth and profitability.
Also Read: The Future of Export Financing: Trends and Innovations
What is Export Finance?
Export finance refers to the financial solutions utilized by businesses to secure sufficient funds for their international trade operations. It enables exporters to address various requirements such as working capital, production costs, and transaction expenses associated with selling goods overseas. Essentially, export finance ensures that businesses have the necessary financial resources to manufacture, ship, and deliver products to foreign markets within budget constraints.
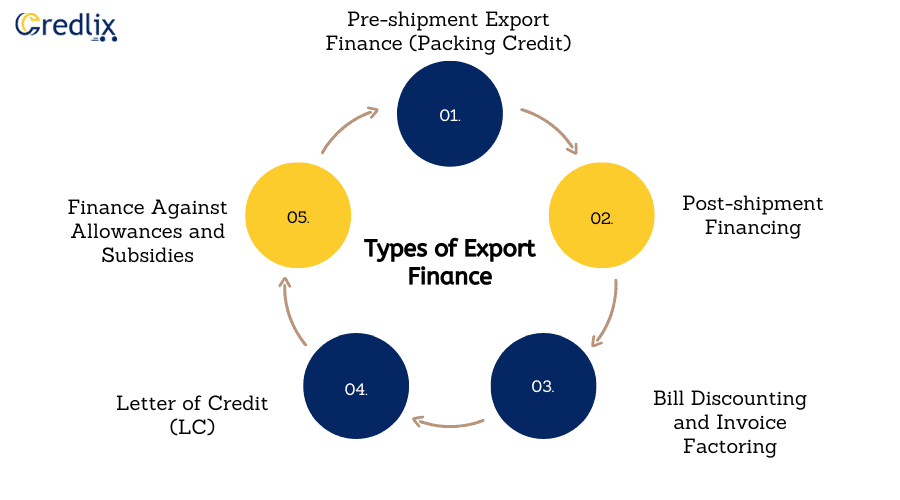
Types of Export Finance
Here’s an elaboration on the types of export finance mentioned:
Pre-shipment Export Finance (Packing Credit)
Pre-shipment export finance, often referred to as packing credit, is extended to exporters to finance the purchase of raw materials, components, and labor required for the production of goods intended for export. This form of financing is typically provided by banks or financial institutions against a confirmed export order or a letter of credit issued by an importer.
The funds obtained through packing credit enable exporters to commence production and fulfill export commitments without facing cash flow constraints. Once the goods are manufactured and shipped, the packing credit is adjusted or repaid using proceeds from the export sale.
Post-shipment Financing
Post-shipment financing is available to exporters after the shipment of goods has been made. This type of financing helps exporters bridge the gap between the shipment of goods and the receipt of payment from the importer. Post-shipment finance can take various forms, including advances against export bills, negotiation of export documents, or discounting of export bills.
By providing immediate access to funds, post-shipment financing enables exporters to meet working capital requirements, manage cash flow, and fulfill additional export orders without waiting for payment from buyers.
Bill Discounting and Invoice Factoring
Bill discounting and invoice factoring are financing techniques that allow exporters to convert their accounts receivable into immediate cash. In bill discounting, the exporter presents export documents, such as bills of exchange or invoices, to a bank or financial institution for early payment at a discounted rate. The bank then assumes the responsibility for collecting payment from the importer.
Similarly, invoice factoring involves selling export invoices to a factoring company at a discount, which then advances a percentage of the invoice value to the exporter upfront. Both bill discounting and invoice factoring provide exporters with liquidity to support ongoing business operations and finance future export activities.
Letter of Credit (LC)
A letter of credit (LC) is a financial instrument issued by a bank on behalf of an importer, guaranteeing payment to the exporter upon presentation of compliant shipping documents. In international trade, letters of credit serve as a secure method of payment, providing assurance to exporters that they will receive payment for goods shipped to foreign buyers.
Exporters can utilize letters of credit to mitigate credit risk, ensure timely payment, and facilitate trade transactions with unfamiliar or high-risk buyers. By complying with the terms and conditions of the LC, exporters can minimize the risk of non-payment and enhance their confidence in conducting cross-border trade.
Finance Against Allowances and Subsidies
Exporters may also access financing against allowances and subsidies provided by the government to promote exports or support specific industries. Governments often offer financial incentives such as export credit guarantees, export subsidies, or duty drawback schemes to encourage export activities and enhance the competitiveness of domestic exporters.
Exporters can leverage these allowances and subsidies as collateral to secure financing from banks or financial institutions, thereby augmenting their working capital and investment capabilities for further expansion into international markets.
How Does Export Finance Work?
Export finance operates through a series of steps designed to facilitate international trade transactions efficiently. Here’s a detailed breakdown of how it works:
Assessment of Export Transaction: The process begins with the exporter identifying a potential overseas market and securing a sales contract or purchase order from a foreign buyer. Once the transaction details are established, including the nature of the goods, quantity, price, and delivery terms, the exporter initiates the export finance process.
Financial Planning and Analysis: The exporter assesses the financial requirements of the export transaction, considering factors such as production costs, shipping expenses, customs duties, and any other associated expenses. This step involves conducting a comprehensive analysis to determine the amount of financing needed to execute the transaction successfully.
Selection of Financing Options: Based on the financial analysis, the exporter evaluates various financing options available for international trade. These options may include export credit insurance, letters of credit, export factoring, export working capital loans, or trade finance facilities offered by banks or financial institutions.
Application for Financing: The exporter submits an application for export financing to the chosen financial institution or provider. The application typically includes details of the export transaction, such as the sales contract, purchase order, invoice, shipping documents, and any other relevant information required by the financier.
Evaluation and Approval: The financial institution reviews the exporter’s application, assessing factors such as creditworthiness, the creditworthiness of the foreign buyer, the risk associated with the transaction, and the viability of the export project. Upon approval, the exporter and the financier negotiate the terms and conditions of the financing arrangement.
Disbursement of Funds: Once the financing arrangement is finalized, the financial institution disburses the agreed-upon funds to the exporter. These funds may be provided upfront as a lump sum payment or in stages, depending on the nature of the transaction and the terms of the financing agreement.
Execution of Export Transaction: With the necessary financing in place, the exporter proceeds to execute the export transaction, manufacturing the goods, arranging for transportation, and fulfilling the delivery requirements outlined in the sales contract or purchase order. Throughout the process, the exporter remains in compliance with relevant trade regulations and documentation requirements.
Also Read: Risk Management Strategies for Exporters: A Deep Dive into Export Financing
Why Your Business Requires Export Finance: 6 Vital Indicators
Here are seven vital indicators explaining why export finance is essential for your business:
Expansion Opportunities: Export finance facilitates seizing growth opportunities by providing the necessary capital to expand into new markets. Whether entering emerging economies or established international markets, export financing enables businesses to pursue expansion strategies confidently.
Cash Flow Management: Export finance helps in managing cash flow effectively, especially when dealing with longer payment cycles inherent in international trade. It provides liquidity by advancing funds against export orders or accounts receivable, ensuring smooth operations without disruptions due to delayed payments.
Risk Mitigation: International trade involves various risks, including currency fluctuations, political instability, and payment defaults. Export finance instruments such as export credit insurance and letters of credit help mitigate these risks, safeguarding businesses against potential losses.
Competitive Advantage: Access to export finance enhances a business’s competitiveness in global markets. With sufficient funding, companies can offer competitive pricing, fulfill large orders, and invest in product innovation and marketing strategies, thereby gaining an edge over rivals.
Customer Relationships: Export finance contributes to building strong relationships with overseas customers by offering flexible payment terms and financing options. This fosters trust and loyalty, encouraging repeat business and referrals, which are crucial for sustaining long-term success in international trade.
Compliance Requirements: Export finance ensures compliance with regulatory and legal obligations governing cross-border transactions. Adhering to trade finance regulations and documentation standards not only mitigates legal risks but also enhances credibility and trust among stakeholders, including financial institutions and government authorities.
Capital Efficiency: Leveraging export finance optimizes capital utilization by unlocking liquidity tied up in export receivables. This allows businesses to allocate resources efficiently, fund growth initiatives, and seize profitable opportunities without straining internal cash reserves or resorting to expensive borrowing options.
Benefits of Export Finance for Exporters
Export finance offers a multitude of benefits for exporters, empowering them to thrive in the global marketplace. Here are twelve key advantages of export finance, elaborated upon:
Enhanced Cash Flow: Export finance provides exporters with immediate access to funds, improving cash flow by accelerating the conversion of export receivables into cash. This liquidity enables exporters to cover operating expenses, invest in growth opportunities, and meet financial obligations without delays or disruptions.
Risk Mitigation: Export finance instruments such as export credit insurance and letters of credit help exporters mitigate various risks associated with international trade. These tools protect against payment defaults, currency fluctuations, political instability, and other uncertainties, safeguarding exporters from potential financial losses.
Expansion into New Markets: With export finance, exporters can confidently explore and enter new international markets. The availability of financing enables businesses to invest in market research, establish distribution channels, and adapt products or services to meet the needs of diverse global consumers, facilitating market expansion and revenue growth.
Competitive Advantage: Access to export finance gives exporters a competitive edge in the global marketplace. By offering flexible payment terms, competitive pricing, and value-added services, exporters can attract customers, secure contracts, and differentiate themselves from competitors, positioning their businesses for long-term success.
Increased Sales and Revenue: Export finance facilitates larger and more frequent export transactions, leading to increased sales volumes and revenue generation for exporters. With sufficient funding, businesses can fulfill larger orders, scale production capacity, and capitalize on demand in foreign markets, driving business growth and profitability.
Customer Satisfaction: Export finance allows exporters to offer favorable payment terms and financing options to overseas buyers, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty. By accommodating diverse payment preferences and providing financing solutions tailored to customers’ needs, exporters can strengthen relationships, encourage repeat business, and build a loyal customer base.
Optimized Working Capital Management: Export finance optimizes working capital management for exporters by providing access to funds tied up in export receivables. This liquidity enables businesses to maintain sufficient working capital levels, finance production cycles, and manage inventory effectively, ensuring smooth operations and sustainable growth.
Access to Global Supply Chains: Export finance facilitates participation in global supply chains by providing the financial resources needed to fulfill export orders and meet supply chain requirements. This enables exporters to collaborate with international partners, fulfill contractual obligations, and capitalize on opportunities for collaboration and integration within global supply networks.
Compliance with Trade Regulations: Export finance helps exporters navigate complex trade regulations and compliance requirements governing international trade. Financial institutions offering export finance services often provide expertise and assistance in ensuring compliance with export documentation, customs procedures, and regulatory standards, minimizing the risk of penalties or delays.
Diversification of Revenue Streams: Export finance enables exporters to diversify their revenue streams by tapping into multiple international markets. Diversification reduces reliance on domestic markets and mitigates risks associated with economic downturns or geopolitical uncertainties, ensuring business resilience and stability in the face of market volatility.
Access to Financing at Competitive Rates: Export finance offers access to financing solutions tailored to the needs of exporters, often at competitive interest rates and favorable terms. This allows exporters to leverage financing efficiently, optimize cost structures, and maximize returns on investment, enhancing overall financial performance and profitability.
Facilitation of Trade Finance Transactions: Export finance streamlines trade finance transactions, simplifying the process of conducting international trade and reducing administrative burdens for exporters. By providing seamless access to trade finance instruments and services, exporters can focus on core business activities, accelerate transaction processing, and enhance operational efficiency.
Final Note
Export finance plays a pivotal role in enabling exporters to thrive in the global marketplace by providing essential financial support, mitigating risks, and unlocking opportunities for growth and expansion. From pre-shipment financing to post-shipment solutions, exporters benefit from enhanced cash flow, improved competitiveness, and streamlined trade transactions. Leveraging various types of export finance empowers businesses to navigate the complexities of international trade successfully, ensuring resilience, profitability, and sustainable success in today’s dynamic global economy.
Also Read: The Role of Export Credit Agencies in Export Financing
[/vc_column_text][vc_empty_space height=””][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/3″ offset=”vc_hidden-sm vc_hidden-xs” el_class=”post-col” css=”.vc_custom_1638872146414{padding-left: 50px !important;}”][vc_widget_sidebar sidebar_id=”consulting-right-sidebar” el_id=”single-right-siebar”][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text][/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row css=”.vc_custom_1638349264629{padding-top: 100px !important;padding-bottom: 80px !important;}”][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”Related Post” font_container=”tag:h2|font_size:25px|text_align:center|color:%233c3c3c” google_fonts=”font_family:Poppins%3A300%2Cregular%2C500%2C600%2C700|font_style:600%20semi-bold%3A600%3Anormal” css=”.vc_custom_1638774169659{margin-bottom: 30px !important;}”][vc_raw_html]JTVCc21hcnRfcG9zdF9zaG93JTIwaWQlM0QlMjIxMDAwNSUyMiU1RA==[/vc_raw_html][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]